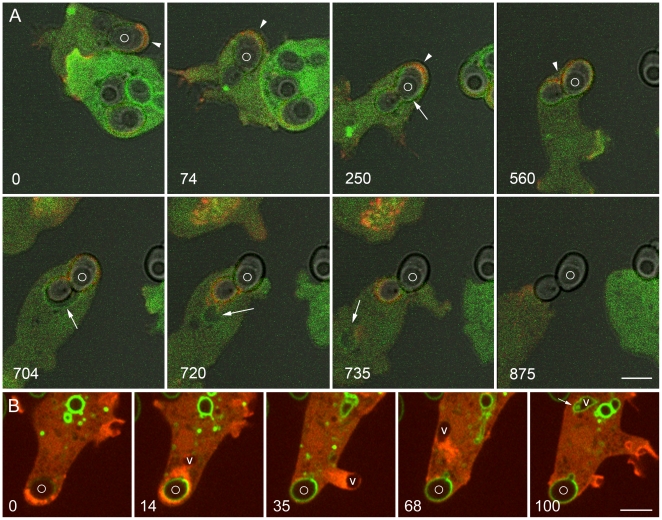
Figure 11. Changes in the phosphoinositide composition of the phagosome and vacuole in premature exocytosis.
A, these Dictyostelium cells, expressing PHcrac-GFP and mRFP-LimEΔ, were mixed with unlabeled yeast one and a half hours earlier. The upper, more weakly labeled cell is migrating. Arrowheads indicate the direction of cell movement or attempted movement in the first four panels. A phagosome containing a budded phagosome (marked with a circle) is initially pushed along by actin assembly (red), but the phagosome becomes increasingly constrained and presently ceases to move. At the same time, PHcrac-GFP begins to bind to the phagosome membrane (tailed arrow in 250-second panel), indicating the presence of PI(3,4,5)P3 and/or PI(3,4)P2. This biosensor also labels the expanded phagosome (704 seconds) and the vacuole that separates from it (720 and 735 seconds) (tailed arrows). Meanwhile, the phagosome is exocytosed. B, this Dictyostelium cell, expressing GFP-2FYVE and mRFP-LimEΔ, was mixed with FITC-yeast 4 hours earlier. At 0 seconds it contains a phagosome in which the FITC-yeast is barely visible, indicating that the phagosome is acidic. At 14 seconds the FITC-yeast has brightened, indicating a rise in pH within the phagosome, and a vacuole (V) has separated from the phagosome. The vacuole moves rapidly away from the phagosome at the head of a trail of actin filaments, creating a protrusion in plasma membrane at 35 seconds, then rebounding to the cytoplasm at 68 seconds. By 100 seconds the vacuole is binding GFP-2FYVE and has assumed the elongated morphology of an early endosome. Meanwhile the FITC-yeast has been exocytosed. Movie S13 shows the complete time series. A, Zeiss LSM510 microscope; B, Perkin-Elmer Ultra View microscope. Bars, 5 µm.