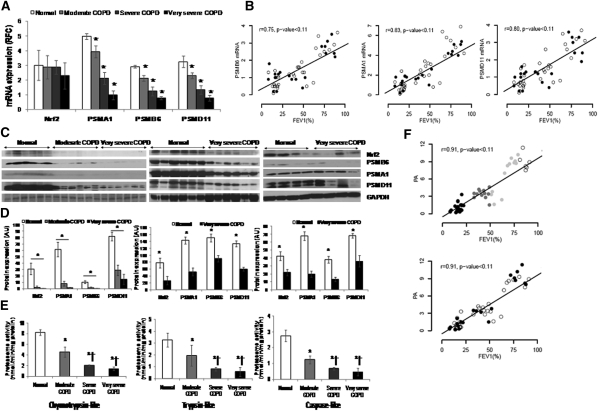
Figure 4.
Proteasomal activity and immunoblot analysis of nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 (Nrf2) and Nrf2-regulated proteasomal subunits in peripheral lung tissue from normal control subjects and patients with mild and advanced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). (A) mRNA expression of Nrf2, PSMA1, PSMB6, and PSMD11 in lungs of normal subjects (n = 17) and patients with moderate (n = 12), severe (n = 12), and very severe COPD (n = 24). *Significant when compared with normal control subjects as analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), P < 0.01. (B) Spearman correlation analysis showed a significant correlation between lung function (FEV1%) and proteasomal subunit mRNAs, colored based on smoking status. Open circles represent ex-smokers and solid circles represents current smokers. The line represents the dose–response relationship based on simple linear models on FEV1% versus log2 proteasomal activity. r = Spearman correlation coefficient. (C) Immunoblot analysis of Nrf2 and Nrf2-regulated PSMA1, PSMB6, and PSMD11 in lung lysates from patients with normal, moderate, and very severe COPD. Glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was loading control. Immunoblot on the left consists of smoker normal, smoker moderate COPD, and smoker very severe COPD (n = 6/phenotype). Immunoblot in the center consists of six normal (nonsmokers [n = 3], ex-smoker [n = 1], and current smokers [n = 2]) and six very severe COPD lungs (ex-smokers [n = 4] and current smokers [n = 2]). Immunoblot on the right consists of four normal (nonsmokers [n = 2], ex-smoker [n = 1], current smoker [n = 1]) and four very severe COPD (ex-smokers [n = 2] and current smokers [n = 2]). (D) Densitometry analysis of corresponding immunoblots normalized to GAPDH using ImageJ software. Data represent mean ± SD of arbitrary units. *Significant compared with normal control subjects as analyzed by one-way ANOVA, P < 0.01. (E) Proteasomal activity (chymotrypsin-like, trypsin-like, and caspase-like) measured as described in Methods in total lung lysates obtained from normal subjects (n = 17) and patients with moderate (n = 12), severe (n = 12), and very severe COPD (n = 24). Data are presented mean ± SD (nmol/min/mg protein). *Significant when compared with normal control subjects; and †significant when compared with moderate COPD as analyzed by one-way ANOVA, P < 0.001. (F) Spearman correlation analysis showing a significant correlation between lung function (FEV1%) and proteasomal activity based on COPD status in the top panel and smoking status in the bottom panel. In the top panel, open circles represent normal lungs, shaded circles represent moderate COPD, and solid circles represent very severe COPD. The line represents the dose–response relationship based on simple linear models on FEV1% versus log2 proteasomal activity. r = Spearman correlation coefficient. In the bottom panel, open circles represent ex-smokers and solid circles represent current smokers. The line represents the dose–response relationship based on simple linear models on FEV1% versus log2 proteasomal activity. r = Spearman correlation coefficient.