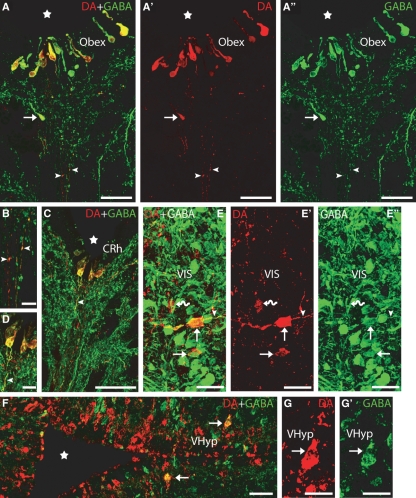
Fig. 2.
Transverse sections of the brain showing DA (red) and GABA (green) immunoreactivities. (A–A′′) Photomicrographs of a transverse section at the transition between the spinal cord and rhombencephalon (obex) showing double-labelled CSF-c cells in the ventral midline, close to the fourth ventricle. Note the presence of a DA-ir/GABA-ir cell ventral to the ependyma (arrow). Note also the presence of double-labelled thin fibres coursing in the raphe (arrowheads). (B) Detail of the double-labelled fibres of A. (C) Photomicrograph of a transverse section of the caudal rhombencephalon showing double-labelled CSF-c cells. Note the presence of a double-labelled process arising from a DA-ir/GABA-ir CSF-c cell (arrowhead). (D) Detail of C. (E–E′′) Photomicrographs of a transverse section of the rostral rhombencephalon showing double-labelled cells in the ventral isthmus (arrows). Note the presence of a dopaminergic cell not labelled by the anti-GABA antibody (curved arrow). Also note the presence of a double-labelled axonal-like process arising from one of the DA-ir/GABA-ir cells (arrowhead). (F) Photomicrograph of a transverse section of the ventral hypothalamus showing double-labelled cells (arrows) in addition to a number of singly GABA-ir and DA-ir cells. (G–G′) Detail of a double-labelled cell from F. Stars indicate the ventricle. Dorsal is up in A–E′ and right in F–G′. CRh, caudal rhombencephalon. For other abbreviations, see the legend to Fig. 1. Scale bars: 50 μm in A–A′′, C and F; 25 μm in E–E′′; and 12.5 μm in B, D and G–G′.