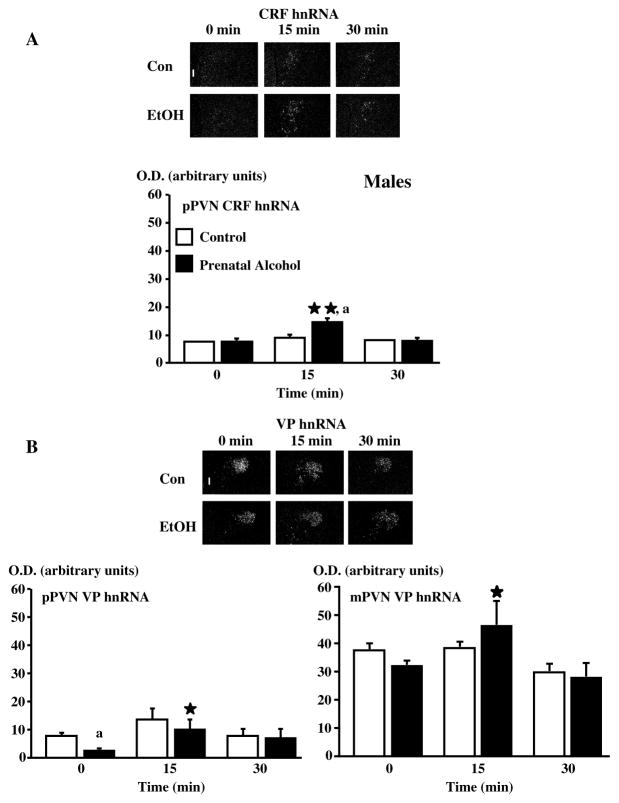
Figure 8.
The PVN CRF neuronal response in response to footshocks is larger in adult adult male FAE offspring, compared to controls. Dark-field photographs of a representative coronal section through the midportion of the PVN of C or E male rats exposed to a 30-min session of mild electrofootshocks and showing increases in CRF hnRNA (A) levels in the pPVN at 15 min and no overall changes in VP hnRNA (B) levels of the pPVN and the mPVN at 15 and 30 min after shocks. Statistical analysis of the data expressed as arbitrary units for optical density (OD) for mRNA levels. Each point represents the mean ± SEM of 4–5 rats. *, P <0.05 and **, P<0.01 vs t=0; a, P<0.01 vs C at the corresponding time. pPVN, parvocellular division of the paraventricular nucleus, mPVN, magnocellular division of the paraventricular nucleus. Magnification, 220×, III, third ventricle. {Adapted by permission from Lee et al.36}