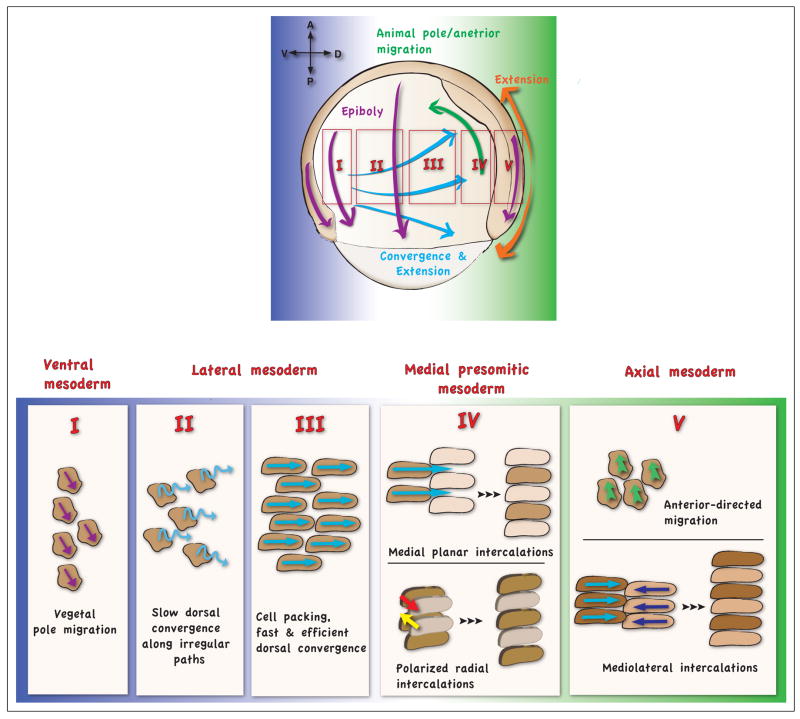
Fig 2. Different cell behaviors along the dorso-ventral axis of the zebrafish gastrula.
During zebrafish gastrulation the cell movements change over time, depending on the gastrulation stage, but also in space, depending on the localization of the cells in particular domains. The midgastrula stage is represented. Several domains can be distinguished along the dorso-ventral gastrula axis according to the type of mesodermal cell movements (showed by magnified I, II, III, IV, V regions). In the most ventral domain (I) the cells undergo migration towards the vegetal pole. In the ventro-lateral domain (II) the cells undergo slow convergence movements along irregular migration paths, as cells located closer to the animal pole bias their trajectories animally and those closer to the vegetal pole bias their trajectories vegetally, the entire population converges and also extends along the anterior-posterior axis. In the lateral domain (III) the cells undergo fast convergence movements along straight migration paths; the cell packing is increased. In the latero-dorsal domain (IV), migration and the cell packing are increased and the cells undergo polarized radial and medio-lateral intercalation movements that drive modest convergence and extension. In the dorsal domain, the most anterior cells undergo anterior directed migration, while more posterior cells undergo massive cell intercalation movements contributing to fast extension and modest convergence.