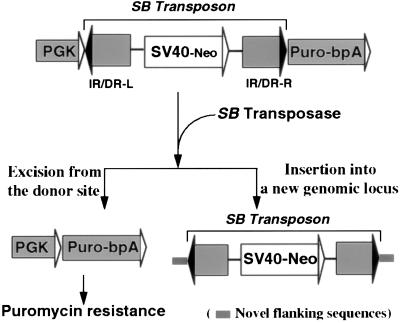
Figure 1.
A genetic-selection strategy for the detection of rare excision events. The puromycin-resistance gene driven by the PGK promoter is inactivated by the insertion of a nonautonomous SB element that separates the promoter from the coding sequence. Excision of the SB element mediated by SB transposase activates the puromycin-resistance gene. The SB element acquires novel flanking sequences when it reintegrates into the genome.