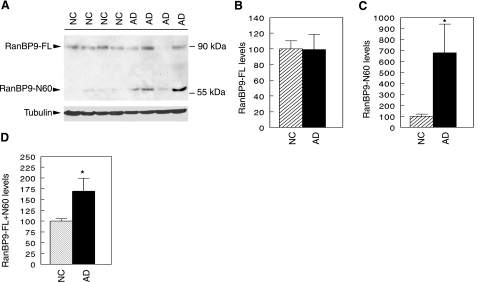
Figure 2.
RanBP9-N60 is robustly increased in AD brains. A) Equal amounts of protein samples from AD brains (n=8) and age-matched normal controls (NC; n=10) were immunoblotted for RanBP9 using anti-RanBP9 antibody. Tubulin was detected with anti-tubulin as a loading control. A representative blot is shown. B) Relative level of full-length RanBP9 (RanBP9-FL) normalized to tubulin. There was no difference in the level of RanBP9-FL normalized to tubulin between AD brain and normal controls. C) Quantitative measurement of the 60-kDa fragment (RanBP9-N60) normalized to tubulin was ∼6-fold higher in AD brains than NC brains, reaching statistical significance. D) When signals from both RanBP9-FL and N60 were combined and normalized to tubulin, there remained ∼75% higher levels in AD brains than in NC brains, which is also highly significant. *P < 0.02.