Figure 6.
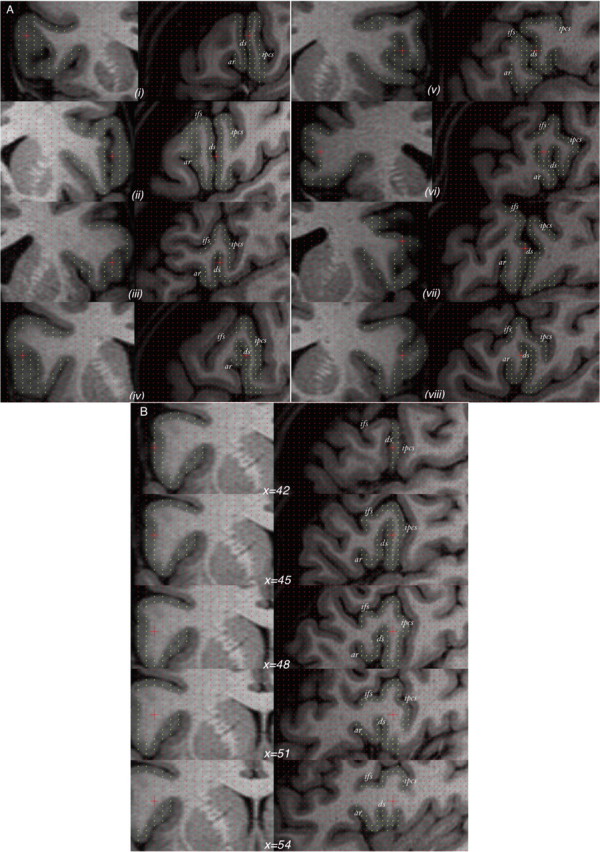
The variability of the diagonal sulcus in humans. A, Eight randomly chosen cases illustrated using orthogonal coronal (left) and sagittal (right) sections. B, Example of one case in which, from the surface of the brain, the anterior ascending ramus is barely visible and could be mistaken for the diagonal sulcus. Only through navigation through the intrasulcal anatomy [indicated through the x (i.e., left–right) dimension] can the anterior ascending ramus be correctly identified. Yellow points mark the frontal operculum. ar, Anterior ascending ramus of the Sylvian fissure; ds, diagonal sulcus; ifs, inferior frontal sulcus; ipcs, inferior precentral sulcus.
