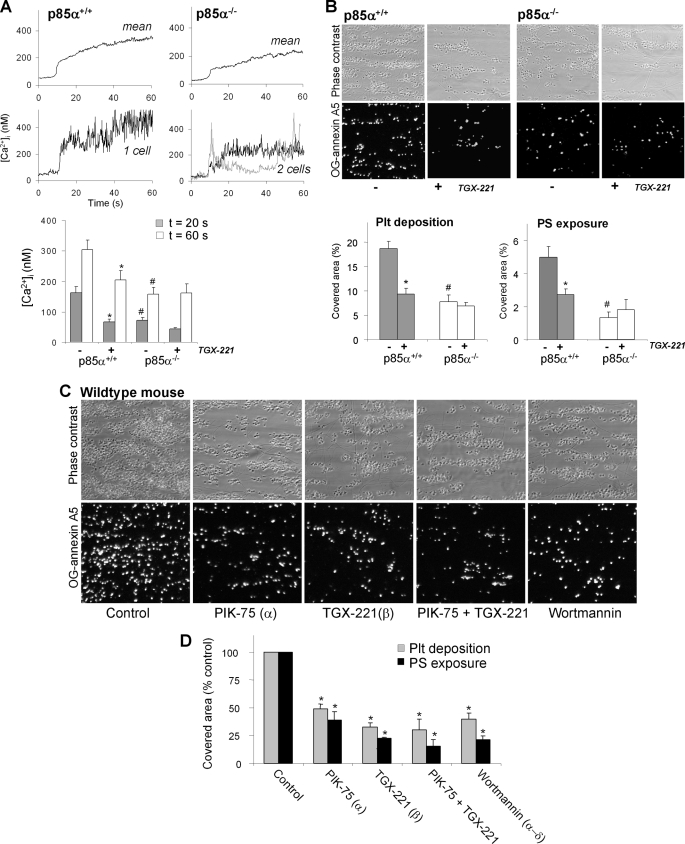
FIGURE 7.
Murine p85α regulates collagen-induced Ca2+ responses and thrombus formation under flow. PPACK/heparin-anti-coagulated blood from p85α+/+ or p85α−/− mice, spiked with 10% Fluo-3-loaded platelets from the same mouse strain, was flowed over collagen at 1000 s−1. The blood was preincubated with Me2SO vehicle or TGX-221 (1 μm). A, contribution of p85α to Ca2+ responses under high shear perfusion. Upper panels: averaged overlays of [Ca2+]i traces from >25 platelets; lower panels: traces from representative single platelets. Bars show quantification of [Ca2+]i increases at 20 s (gray) or 60 s (white) after initial platelet activation. B, contribution of p85α to thrombus formation and PS exposure. Shown are representative images of phase-contrast (120 × 120 μm) and OG-annexin A5 fluorescence (150 × 150 μm) of p85α+/+ and p85α−/− thrombi. Bars represent surface area coverage of all deposited platelets and PS-exposing platelets. C and D, effect of pharmacological PI3K inhibition on thrombus formation and PS exposure. Wild-type blood was preincubated with Me2SO vehicle (control), PIK-75, TGX-221, or wortmannin (each 1 μm). Data are means ± S.E. (n = 3–5); *, p < 0.05 compared with vehicle control; #, p < 0.05 compared with wild type.