FIGURE 3.
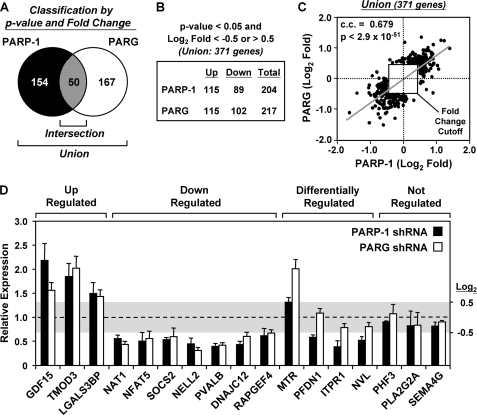
Defining the genes most robustly regulated by PARP-1 and PARG. A, Venn diagram of PARP-1- and PARG-regulated genes after applying a -fold change cutoff of log2 <−0.5 or >0.5. Of the union of 371 genes most robustly regulated by either PARP-1 or PARG, 50 are commonly regulated. B, the distribution of the most robustly up-regulated or down-regulated genes upon knockdown of PARP-1 or PARG is indicated. C, correlation analysis comparing the magnitude and direction of regulation of the 371 most robustly regulated genes shown in A and B. The Spearman correlation coefficient (c.c.), p value, and -fold change cutoff are indicated. D, gene-specific confirmation of the expression microarray results by RT-qPCR. Luc, PARP-1, and PARG knockdown MCF-7 cells were seeded and grown under the same conditions used for the expression microarrays. Total RNA was isolated, reverse-transcribed, and subjected to qPCR using gene-specific primers. Genes were considered to be regulated if the log2 -fold change was <−0.5 or >0.5 (values falling outside of the shaded box). Each bar represents the mean + S.E. (error bars) from three or more independent determinations. All bars with a mean value falling outside of the shaded box are statistically different from the Luc control, as determined by a Student's t test with a p value threshold of <0.05.