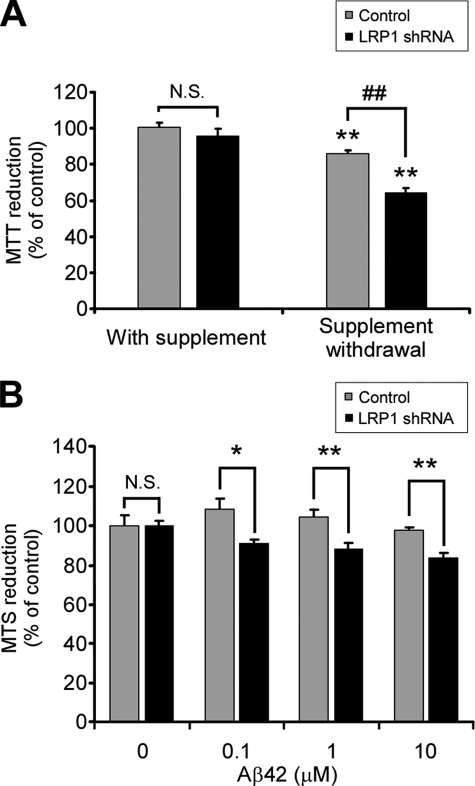
FIGURE 2.
LRP1 knockdown decreases cell viability in primary neurons upon trophic withdrawal and Aβ42-induced toxicity. A, effect of control or LRP1 shRNA on neuronal viability analyzed by the MTT reduction assay in the presence or absence of B27 supplement. Increased neuronal cell death was detected in LRP1 shRNA-infected neurons upon trophic support withdrawal. The mean differences were compared by ANOVA and Dunnett's test using control infection + B27 supplement cells as the reference group (**, p < 0.01) or by ANOVA and Bonferroni's test for selected groups (##, p < 0.01). B, LRP1 knockdown renders neurons susceptible to Aβ-induced toxicity. Primary neurons were infected with control or LRP1 shRNA and incubated with 0, 0.1, 1, and 10 μm Aβ42 for 18 h, and neuronal viability was assessed by reduction of the MTS redox dye. The mean differences were compared by unpaired Student's t test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.