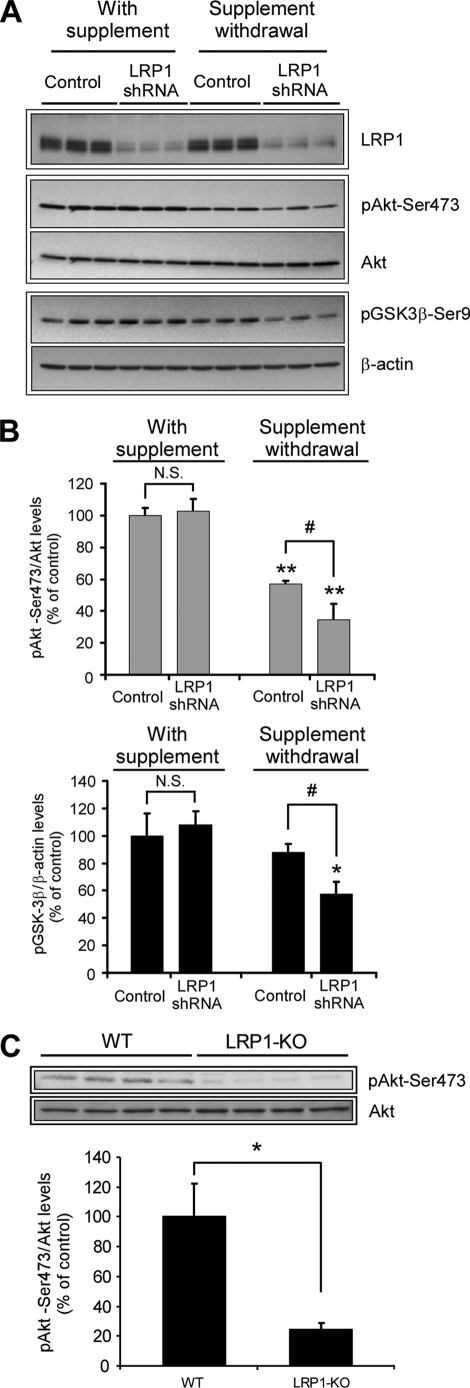
FIGURE 4.
LRP1 regulates Akt phosphorylation in vitro and in vivo. A, decreased phospho-Akt and phospho-GSK-3β levels in LRP1 knocked down neurons upon trophic withdrawal. Primary neurons were infected with control or LRP1 shRNA, and the levels of LRP1, phospho-Akt (Ser473), total Akt, and phospho-GSK-3β were analyzed by Western blot under both control conditions and upon 18 h of treatment with neurobasal-only media. The β-actin levels were determined as a loading control. The levels of phospho-Akt and phospho-GSK-3β were additionally decreased in LRP1 knocked down neurons upon trophic withdrawal. B, protein levels from experiments in A were determined by densitometry, and the corresponding phospho-Akt to total Akt and phospho-GSK-3β to β-actin ratios were calculated and plotted relative to control neurons. The mean differences were compared by ANOVA and Dunnett's test using control infection + B27 supplement treated cells as the reference group (**, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05) or by ANOVA and Bonferroni's test for selected groups (#, p < 0.05). C, decreased phospho-Akt in LRP1 forebrain knock-out mice. Equal amounts of total brain homogenates (40 μg) from LRP1 forebrain knock-out mice and littermate controls were subjected to Western blot analysis, and both phospho-Akt (Ser473) and total Akt levels were determined (n = 4). Lower panel, densitometric analysis of phospho-Akt and total Akt levels determined from experiments as in A. The mean differences were compared by unpaired Student's t test, * p < 0.05. WT, wild type.