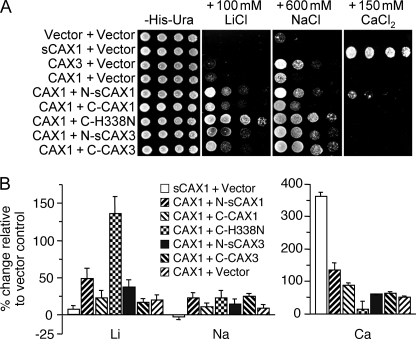
FIGURE 6.
Functionality of CAX1 and CAX3 when co-expressed with CAX half proteins. A, suppression of Li+, Na+, and Ca2+ sensitivity of K667 yeast cells expressing sCAX1, CAX1, or CAX3, or co-expressing CAX1 with sCAX1 N-terminal half protein (N-sCAX1), CAX1 C-terminal half protein (C-CAX1), sCAX3 N-terminal half protein (N-sCAX3), CAX3 C-terminal half protein (C-CAX3), or CAX1H338N C-terminal half protein (C-H338N). Saturated liquid cultures of K667 yeast were diluted in stepwise 5-fold dilutions and then spotted onto selection medium or YPD medium containing either 150 mm CaCl2, 100 mm LiCl, or 600 mm NaCl. Yeast cells expressing empty vector were used as a negative control. The plates were incubated and photographed after 2 days at 30 °C. B, Li+, Na+, and Ca2+ ion content analysis in K667 yeast cells co-expressing sCAX1 or CAX1 with vector or CAX1 in combination with N-sCAX1, C-CAX1, N-sCAX3, C-CAX3, or C-H338N grown to stationary phase in YPD medium supplemented with 500 μm LiCl (for the Li+ and Na+ content measurements) or 10 mm CaCl2 (for the Ca2+ content measurements). The data from five repeats were calculated with a formula: (Ioncax − Ionvector)/Ionvector × 100, and expressed as the means ± S.E. (n = 5). As discussed previously, the ion content fluctuated depending on the growth medium used.