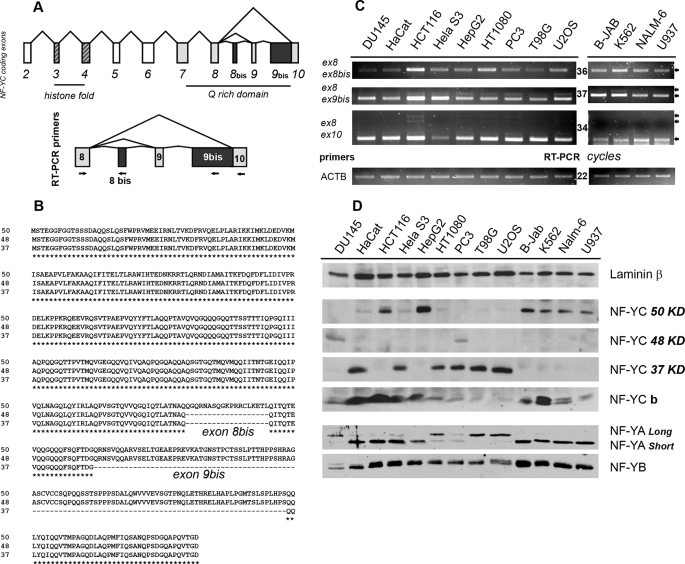
FIGURE 1.
Identification of new NF-YC splicing isoforms. A, upper panel, genomic structure of the NF-YC coding sequence. Exons coding for the HFM domain are striped; the ones coding for the Q-rich domain are gray, and the newly identified exon 8bis and 9bis are black. Lower panel, primers used for RT-PCR experiments are mapped within the NF-YC C terminus. B, sequence alignments of the 37-, 48-, and 50-kDa polypeptides generated by the in silico identified NF-YC mRNAs. C, semi-quantitative RT-PCRs were performed with the indicated NF-YC primer pairs, after normalizing the 13 human cDNA for β-actin content (lower panel). Cell lines are indicated on the top. Ex8-Ex10 PCR product corresponds to the 37-kDa isoform, Ex8-Ex9bis to the 48-kDa isoform, and Ex8-Ex8bis to the 50-kDa NF-YC. RT-PCRs were performed in the linear range of amplification; number of cycles for each product is indicated in the middle. D, Western blots analysis performed with anti NF-YA, NF-YB, and NF-YC antibodies, on nuclear extract derived from the same 13 cell lines used for RT-PCRs. β-Laminin was used as an internal control for nuclear extracts loading (upper panel).