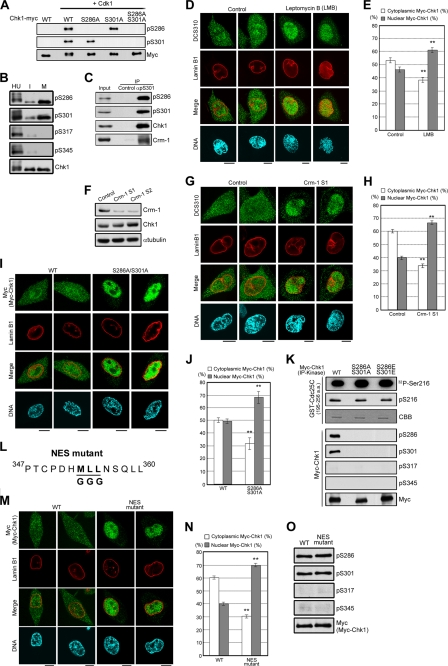
FIGURE 2.
Chk1 transport to the cytoplasm is regulated not only by Crm-1-dependent nuclear export but also by Cdk1-induced Chk1 phosphorylation. A, each glutathione S-transferase-Chk1-Myc construct incubated with or without cyclin B1-Cdk1 (10, 13) was subjected to the immunoblotting. B and C, interphase (I), mitotic (M), or hydroxyurea (HU)-treated HeLa cells were prepared as described (10, 13). Immunoprecipitation (IP) of Chk1 from cell extracts (B) or of Ser301-phosphorylated Chk1 from mitotic cell extracts (C) was performed as described (13). d--J, M, and N, HeLa cells were treated with 2 ng/ml leptomycin B or an equal volume of 70% ethanol (control) for 1 h (D and E). HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs for 48 h (F–H); there was only a marginal difference in Chk1 localization between Crm-1 S1 and S2 (data not shown). Tet-On HeLa cell lines were treated with doxycycline to introduce exogenous Myc-tagged WT Chk1, S286A/S301A, or the NES mutant (I, J, M, and N). Cells were stained with DCS310 (D and G) or anti-Myc antibody (I and M, green). Nuclear membranes and DNA were simultaneously stained with anti-lamin B1 antibody (red) and DAPI (blue), respectively (D, G, I, and M). Scale bars = 10 μm. The bar graphs show the cytoplasmic or nuclear proportion of DCS310 (E and H) or anti-Myc (J and N) signals. Data represent means ± S.E. for at least 20 cells in cell group. **, p < 0.01 compared with control cells (E and H) or WT-expressing cells (J and N). K, the kinase activity of each Myc-Chk1 construct in mitosis was measured. Myc-Chk1 was purified from each mitotic cell extract as an anti-Myc immunocomplex. The phosphorylation reaction was performed as described previously (5). For the detection of Chk1 kinase activity, each sample was subjected to autoradiography (32P-Ser216, first row) or immunoblotting with anti-phospho-Ser216 antibody in Cdc25C (pS216, second row). As a loading control for each substrate, Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining was performed. For assessment of the Chk1 phosphorylation status in anti-Myc immunoprecipitates, immunoblots were made with anti-phospho-Chk1 and anti-Myc antibodies (lower rows). a.a., amino acids. L, the schema shows the Chk1 mutant (NES mutant) in which the underlined amino acids were changed to Gly. O, each immunoprecipitated Myc-Chk1 construct was subjected to immunoblotting.