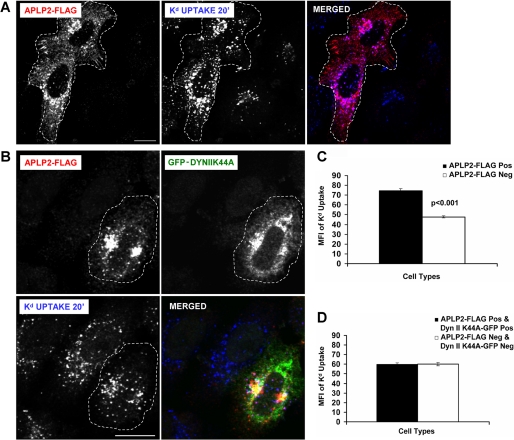
FIGURE 3.
Blocking clathrin-mediated endocytosis by expression of dynamin II K44A prevented APLP2 from increasing Kd endocytosis. A, HeLa-etKd cells transfected transiently with APLP2-FLAG (but not GFP-dynamin II K44A) for 24 h were pulsed with 34-1-2 Ab for 20 min in complete medium. At the end of the pulse period, non-internalized cell surface-bound Abs were removed. After fixation, the cells were stained with rabbit anti-FLAG Ab for 1 h. The cells were incubated with Alexa Fluor 568 goat anti-rabbit Ab to identify APLP2-FLAG and Alexa Fluor 405 goat anti-mouse Ab to identify 34-1-2-bound Kd. Red, APLP2-FLAG; blue, Kd. Bar corresponds to 10 μm. Cells expressing APLP2-FLAG are encircled with a dashed white line. B, the same procedure described in A was followed except that the HeLa-etKd cells were co-transfected transiently with both APLP2-FLAG and GFP-dynamin II K44A for 24 h. Red, APLP2-FLAG; green, GFP-dynamin II K44A; blue, Kd. Bar corresponds to 10 μm. Cells co-expressing APLP2-FLAG and GFP-dynamin II K44A are encircled with a dashed white line. C, ImageJ software was used to measure the internalized Kd fluorescence for >80 cells transfected with APLP2-FLAG versus no APLP2-FLAG. Note that in this control no cells were transfected with GFP-dynamin II K44A, and APLP2-FLAG was able to increase Kd endocytosis. D, Image J software was used to measure the internalized Kd fluorescence for >80 cells expressing both APLP2-FLAG and GFP-dynamin II K44A, as well as >80 cells expressing neither protein. In this case, some of the cells expressed GFP-dynamin II K44A, and APLP2-FLAG was not able to increase Kd endocytosis if GFP-dynamin II K44A was also expressed in the same cell. C and D, mean fluorescence intensities and mean ± S.E. were calculated, and p values were determined by Student's paired t test: C, p < 0.001; D, p = 0.81.