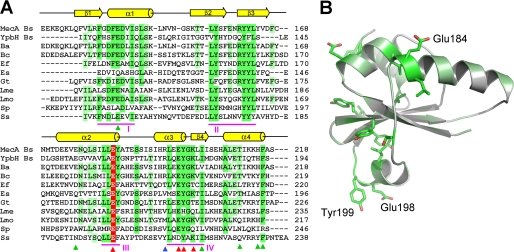
FIGURE 3.
Sequence alignment identifies conserved regions in MecA. A, sequence alignment of MecA with 10 other homologous proteins. Conserved amino acids are colored green and light green. Red, blue, and green arrows denote those residues whose mutations result in loss, partial loss, and no loss of MecA degradation, respectively. YpbH (accession code: GenBankTM CAB14213) is also from B. subtilis. The other MecA homologues are from: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (Ba, ABS73516), Bacillus coahuilensis (Bc, ABFU01000021), Geobacillus thermodenitrificans (Gt, ABO66079), Enterococcus faecalis (Ef, AAO82382), Exiguobacterium sibiricum (Es, ACB61267), Leuconostoc mesenteroides (Lme, ABJ62794), Listeria monocytogenes (Lmo, CAD00268), Streptococcus pneumoniae (Sp, ACH47966), and Staphylococcus saprophyticus (Ss, BAE18932). B, highly conserved amino acids map to one side of the MecA-(121–218) structure. The three labeled amino acids, Glu-184, Glu-198, and Tyr-199, are likely to play a key role in binding to ClpC. Mutation of these amino acids led to weakened interaction with ClpC and subsequent loss of functions.