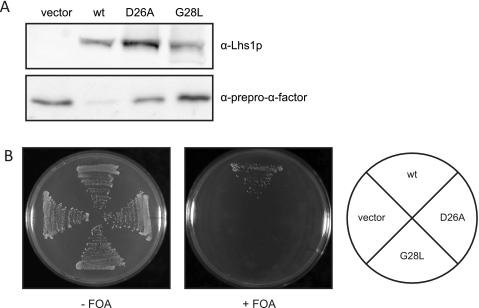
FIGURE 8.
The D26A and G28L mutations affect Lhs1p function in vivo. A, JTY33 (Δlhs1) transformed with either empty vector or HIS3-based plasmids containing LHS1, lhs1(D26A), or lhs1(G28L) was grown to midlog phase in yeast nitrogen base (YNB) with appropriate supplements. Whole cells extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against Lhs1p and prepro-α-factor. B, the ability of the Lhs1p mutant to complement the lethal defect associated with the Δire1Δlhs1 double mutation was examined by transforming JTY44 (Δire1Δlhs1) containing pRC43 (LHS1, URA3) with either empty vector or HIS3-based plasmids containing LHS1, lhs1(D26A) or lhs1(G28L), followed by counterselection of pRC43 on 5′-fluoroorotic acid (FOA) medium.