FIGURE 3.
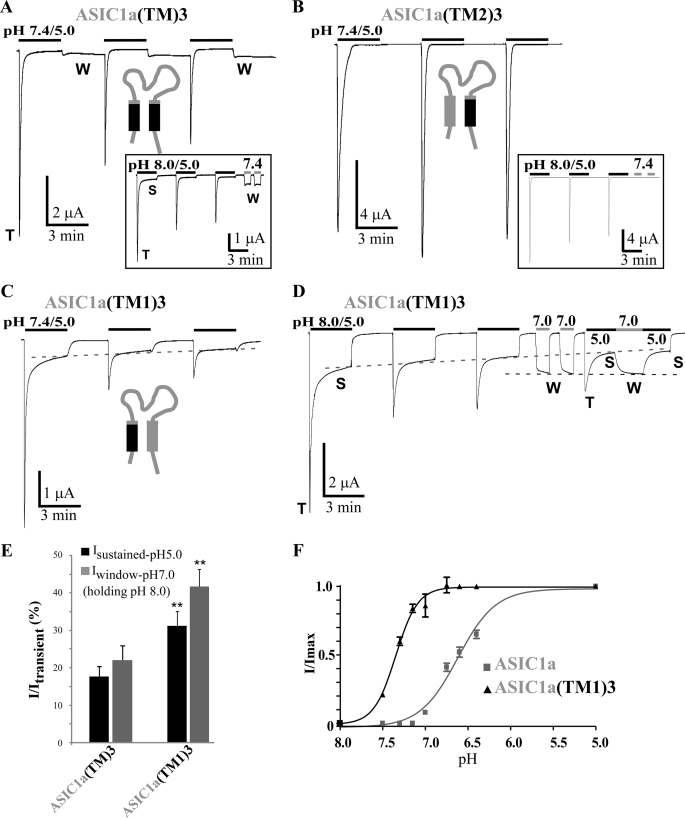
Analysis of the role of the transmembrane domains in generation of the sustained current in ASIC1a/3 chimeras. A, B, and C, representative current traces of pH 5. 0-activated currents recorded at −50 mV from Xenopus oocytes injected with ASIC1a(TM)3 (A), ASIC1a(TM2)3 (B), and ASIC1a(TM1)3 (C). Three pH pulses of 3 min each are made at 3-min intervals from a holding pH of 7.4. Inset in A and B, Similar recordings made from a holding pH of 8.0 instead of 7.4. Two successive pH pulses from 8.0 to 7.4 have been used at the end of the recordings to check for the presence of a window current. T, S, and W, transient, sustained, and window components, respectively. D, typical current trace of the ASIC1a(TM1)3 chimera recorded as in C but from a holding pH of 8.0 instead of 7.4, followed by the activation of the window current at pH 7.0 and of the pH 5.0-evoked sustained current. The dashed lines illustrate the slow decrease of the pH 5.0-evoked sustained current and the steady-state of the pH 7.0-activated window current. E, average relative pH 5.0-evoked sustained current and pH 7.0-evoked window currents (holding pH of 8.0). pH 5.0-evoked sustained current were measured 45 s after the peak activated by the first pH pulse as shown in A–C, for ASIC1a(TM)3 and ASIC1a(TM1)3 (n = 30 and 35, respectively). Average relative pH 7.0-evoked window currents for ASIC1a(TM)3 and ASIC1a(TM1)3 (n = 22 and 35, respectively) are shown. The ASIC1a(TM2)3 chimera, which is lacking both pH 5.0-activated and pH 7.0- and pH 7.4-evoked window currents, is not included in this graph. **, p < 0.01, significantly different from ASIC1a(TM)3. F, pH-dependent activation curves of the transient current associated with ASIC1a and the ASIC1a(TM1)3 chimera. pH has been decreased from pH 8.0 to the indicated pH values (7.5/7.3/7.15/7.0/6.75/6.6/6.4/5.0) and normalized to pH 5.0. The pH0.5 values for activation of ASIC1a and ASIC1a(TM1)3 are 6.62 ± 0.02 and 7.34 ± 0.02, n = 8 and 7, respectively.