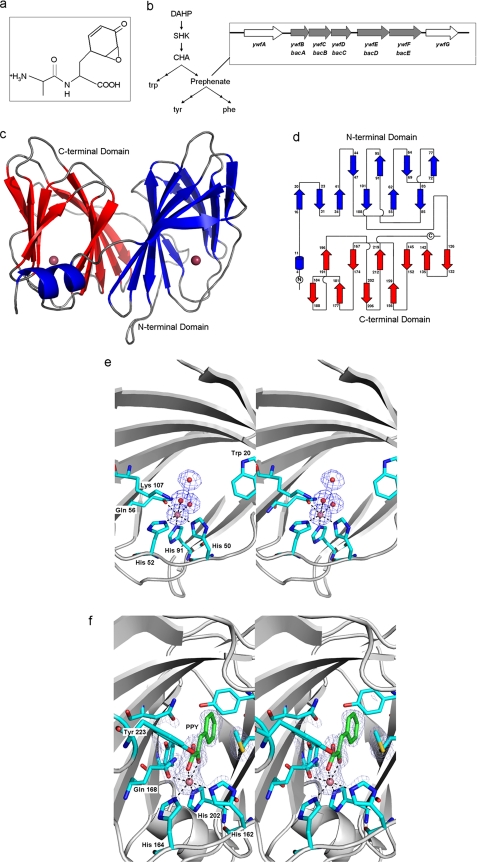
FIGURE 1.
BacB in the context of the bac operon of B. subtilis. a, di-peptide antibiotic bacilysin has an N-terminal alanine and anticapsin at the C terminus. b, biosynthetic route for bacilysin production branches off the aromatic amino acid biosynthesis pathway at prephenate. c, BacB is a bicupin with two putative active sites, each containing a bound metal ion. d, topology diagram of BacB (23). e, electron density map of the active site of the N-terminal domain. The metal ion along with two water molecules is shown along with residue Lys-107 (at the entrance of the β barrel, shown to be crucial for catalytic activity), and residues His-50, His-52, His-91, and Gln-56 (coordinating the metal ion). f, (Fo − Fc) electron density map at the C-terminal domain could be interpreted as a bound PPY. The metal ion along with the coordinating residues His-162, His-164, His-202, and Gln-168 are shown.