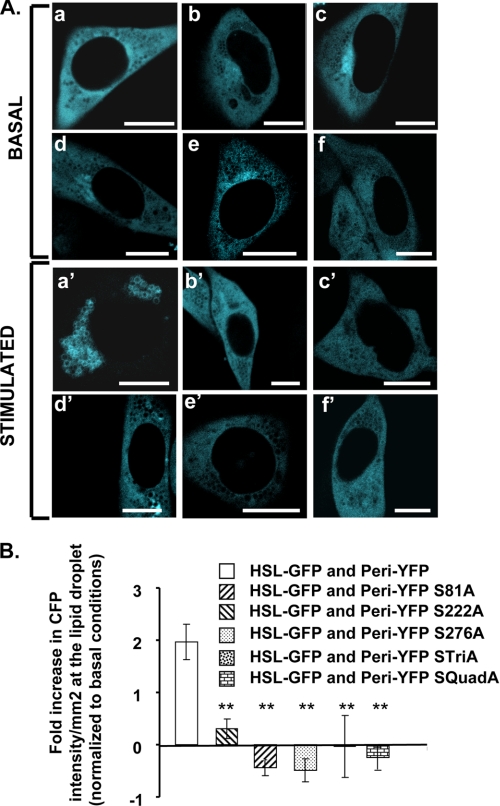
FIGURE 6.
HSL recruitment to lipid droplets requires the phosphorylation of serines 81, 222, and 276 of perilipin A. A, CHO-K1 cells were co-transfected with HSL-CFP and one of the following mutated phosphorylation site perilipin fusion proteins: perilipin-YFP (panels a and a′); perilipin S81A-YFP (panels b and b′); perilipin S222A-YFP (panels c and c′); perilipin S276A-YFP (panels d and d′); perilipin STriA-YFP (Ser-81, Ser-222, and Ser-276 mutated to Ala) (panels e and e′); perilipin SQuadA-YFP (Ser-81, Ser-222, Ser-276, and Ser-433 mutated to Ala) (panels f and f′). Cells were incubated overnight with 400 μm oleic acid. The following day, the cells were incubated with 5 μm triacsin C with no further additions (basal) or were stimulated for 10 min with 10 μm forskolin, 1 mm IBMX, and 5 μm triacsin C; live cells were examined with a confocal microscope as in Fig. 1. Bar, 10 μm. B, quantitative analysis for HSL binding to lipid droplets covered with perilipin A or mutated variants of perilipin. Data are means ± S.E. from 2 to 14 experiments. HSL binding to lipid droplets coated with each of the mutated variants of perilipin was significantly different from the binding of HSL to unmodified perilipin A (**, p < 0.001).