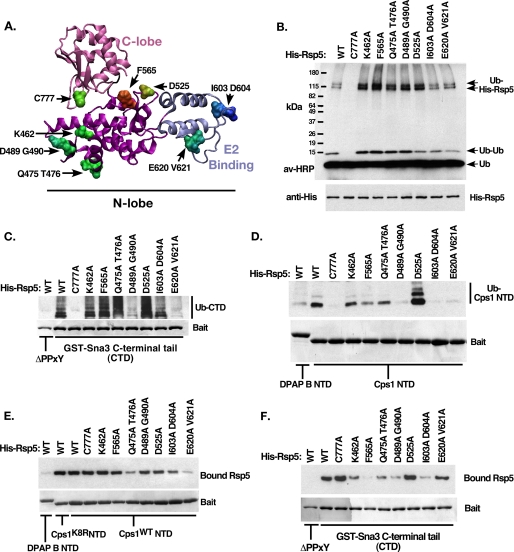
FIGURE 3.
Characterization of Rsp5 N-lobe mutants. A, homology structural model of the Rsp5 HECT domain indicating the location of the C-lobe (pink) and E2 binding domain (blue). Residues selected for site-directed mutation are indicated. B, in vitro autoubiquitination reactions were performed using the indicated form of Rsp5. Ubiquitinated species were detected using avidin-HRP. Bands corresponding to free ubiquitin, di-ubiquitin, and 2 forms of ubiquitinated His-Rsp5 are indicated. C, C-terminal cytoplasmic tail of the PY-motif containing Rsp5 substrate Sna3 was immobilized and included in the ubiquitination reaction as in B. Following the 30-min reaction time, beads were washed with a high-salt buffer to remove bound Rsp5 and other copurifying proteins. Ubiquitinated bound material was visualized as in B, while baits were visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. The PY-mutant form of Sna3 tail was used as a negative control. Bands corresponding to ubiquitinated GST-Sna3 C-terminal domain (CTD) are indicated. D, ubiquitination reactions were performed as in C, except the reaction substrates were the cytoplasmic tails of DPAP B NTD (non-Rsp5 substrate) or Cps1 NTD (Rsp5 HECT-interacting substrate) fused to GST. E, Rsp5 binding reactions were performed to correlate the ability of His-Rsp5 mutants to bind Cps1 NTD, reaction conditions were kept identical to D, except that MgATP was omitted to prevent the modification of His-Rsp5. Low salt wash buffer was used to preserve noncovalent interactions. Detection of bound Rsp5 was by anti-His Western blot. F, Rsp5 binding reactions were performed as in E, except with the indicated GST constructs.