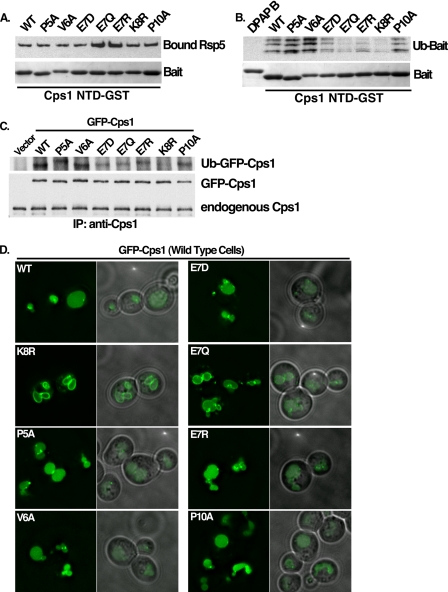
FIGURE 5.
Residues within Cps1 MVB sorting sequence required for a functional interaction with Rsp5. A, Cps1 NTD-GST mutant proteins were tested for their ability to recruit His-Rsp5 in vitro under conditions identical to the ubiquitin reaction (−MgATP) in B. Bound Rsp5 was detected by anti-His western and equivalent loading of GST baits was by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. B, Rsp5 was assessed for its ability to ubiquitinate mutant forms of Cps1 in vitro. After a 30-min ubiquitination reaction in the presence of immobilized substrate, beads were washed with buffer containing 500 mm KOAc to remove noncovalently bound material. Bound, ubiquitinated material was detected with avidin-HRP. Equivalent loading of GST baits was confirmed by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. C, wild type or mutant forms of full-length GFP-Cps1 were co-expressed with HA-ubiquitin in a pep12Δ yeast background to allow detection of in vivo ubiquitin-modified Cps1. Immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-Cps1 polyclonal antibody and ubiquitinated species were detected with anti-HA Western blotting. Anti-GFP Western blot of the same material serves as a loading control. D, same GFP-tagged Cps1 mutants as in C above were examined by fluorescence microscopy for their ability to sort into the MVB pathway in a wild type yeast background as determined by GFP fluorescence in the vacuolar lumen.