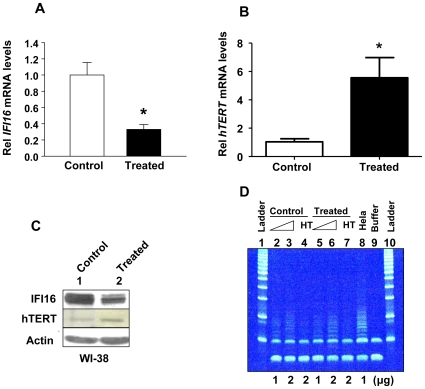
Figure 1. Reduced expression levels of IFI16 protein in aphidicolin-treated human normal diploid fibroblasts are associated with increased expression levels of the hTERT and telomerase activity.
(A and B) Total RNA isolated from untreated (control) or aphidicolin (5 µg/ml for 24 h) treated young WI-38 fibroblasts was subjected cDNA synthesis followed by quantitative real-time PCR using the TaqMan assay for the IFI16 gene (A) or hTERT gene (B). Results are mean values of triplicate experiments and the error bars represent standard deviation (* p<0.05). (C) Total protein extracts prepared from untreated (lane 1) or aphidicolin (5 µg/ml for 24 h) treated (lane 2) young WI-38 fibroblasts were subjected immunoblotting using antibodies specific to the indicated proteins. (D) Extracts containing the indicated amounts (µg) of proteins from control (lanes 2–4) or aphidicolin-treated (lanes 5–7) young WI-38 cells were subjected to TRAPeze assays without any treatment (lanes 2, 3, 5, and 6) or after heat treatment (lanes 4 and 7) to detect the telomerase activity. As controls, extracts from HeLa cells (lane 8) or buffer alone (lane 9) were also included in the assay. The reaction products were subjected to native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis along with DNA fragments of increasing length as size markers (DNA-ladder).