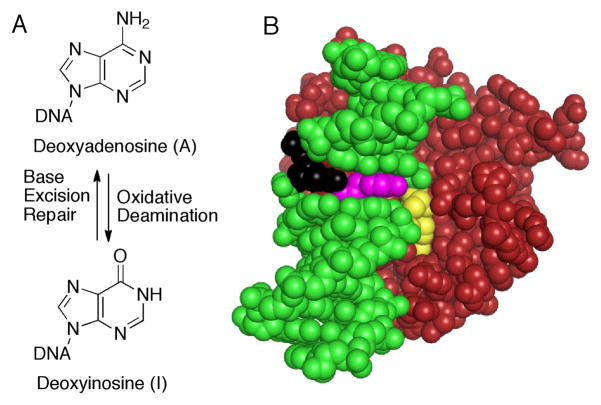
Figure 1.
Deamination of A to form I and structure of AAG bound to damaged DNA. (A) Oxidative deamination of A is reversed by AAG and the base excision repair pathway. (B) AAG is red, the intercalating tyrosine (Y162) is magenta, and the DNA is green, except for the lesion (yellow) that is flipped into the active site and the opposing nucleotide (black). This opposing nucleotide is missing in the bulged substrate. Coordinates are from the PDB for AAG bound to 1,N6-ethenoA-DNA; 1EWN.4