Fig. 2.
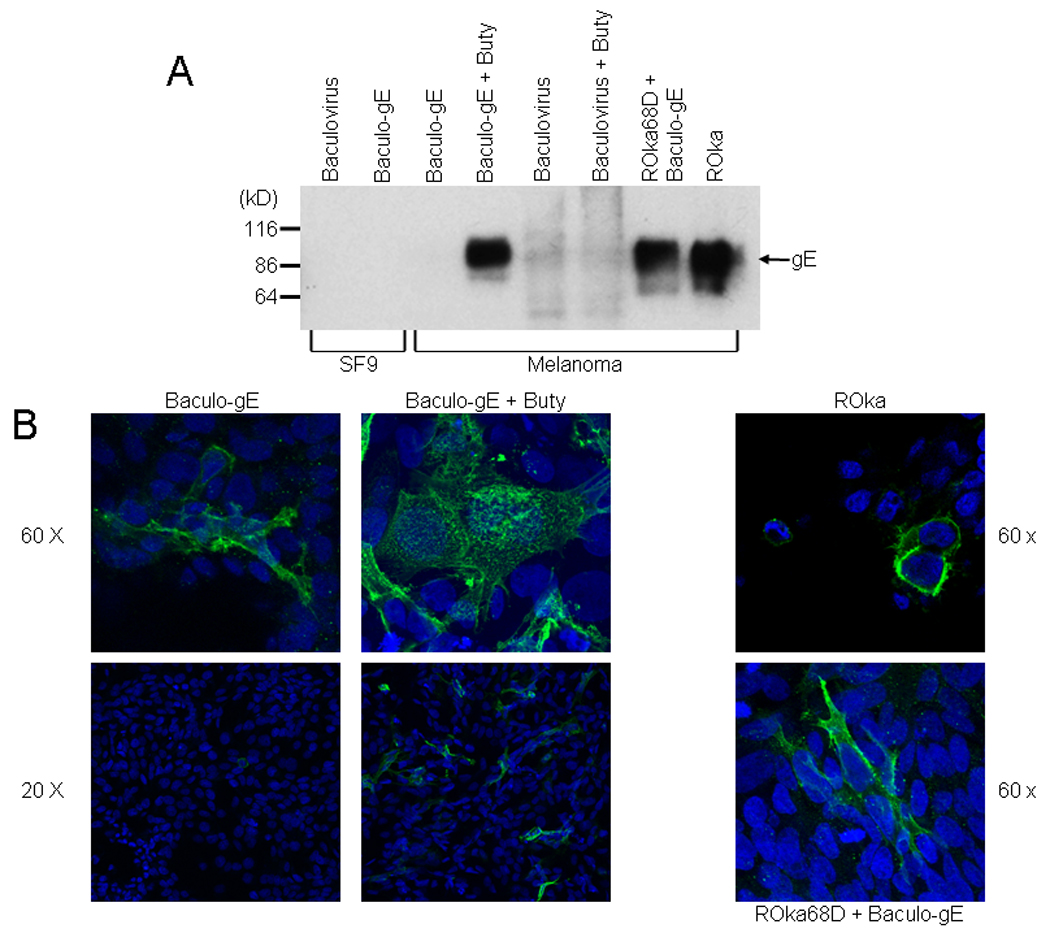
Expression of VZV gE in cells infected with a baculovirus expression vector. (A) Expression of VZV gE in Sf9 or melanoma cells. Sf9 cells were infected with parental baculovirus AcNPV (lane 1) or Baculo gE-RV (lane 2). Melanoma cells were infected with Baculo gE-RV (lanes 3,4) or parental baculovirus (lanes 5,6) in the absence (lanes 3,5) or presence (lanes 4,6) of sodium butyrate (buty). Melanoma cells were infected with Baculo gE-RV in the absence of butyrate followed by VZV ROka68D (lane 7) or with VZV ROka (lane 8). (B) Immunofluorescence microscopy for VZV gE in cells infected with VZV ROka, Baculo gE-RV alone, Baculo gE-RV and sodium butyrate, or Baculo gE-RV followed by ROka68D. Nuclei are stained with DAPI.
