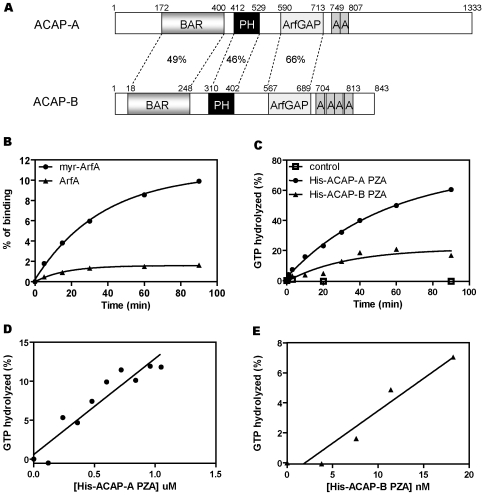
Figure 1. Identification of ACAP-A and ACAP-B as ArfGAP homologs in Dictyostelium.
A, a schematic illustration of ACAP-A and ACAP-B domains. The structure of ACAP-A and ACAP-B was predicted by Pfam database of conserved protein domains. Amino acid sequence identity between each domain of the two proteins is indicated in percentages. B, GTPγS binding to myristoylated (myrArfA) and non-myristoylated ArfA was determined as described under “Methods.” 10 pmol of ArfA or myrArfA was used for each point. Data shown were the average of two experiments. C, time course of ArfGAP activity of Dictyostelium ACAP PZA proteins. His-ACAP-A PZA (0.9 µM) or His-ACAP-B PZA (22.8 nM) was incubated with 0.1 µM [α-32P]GTP-loaded myrArfA at 30°C. Aliquots were withdrawn at the indicated times and GTP hydrolysis measured as described under “Methods.” Data shown were the average of two experiments. D and E, dose dependence of Dictyostelium ACAPs. Different concentrations of His-ACAP-A PZA (D) or His-ACAP-B PZA (E) were incubated with 0.1 µM [α-32P]GTP-loaded myrArfA at 30°C for 90 min. Results shown were the average of at least two experiments.