Figure 1.
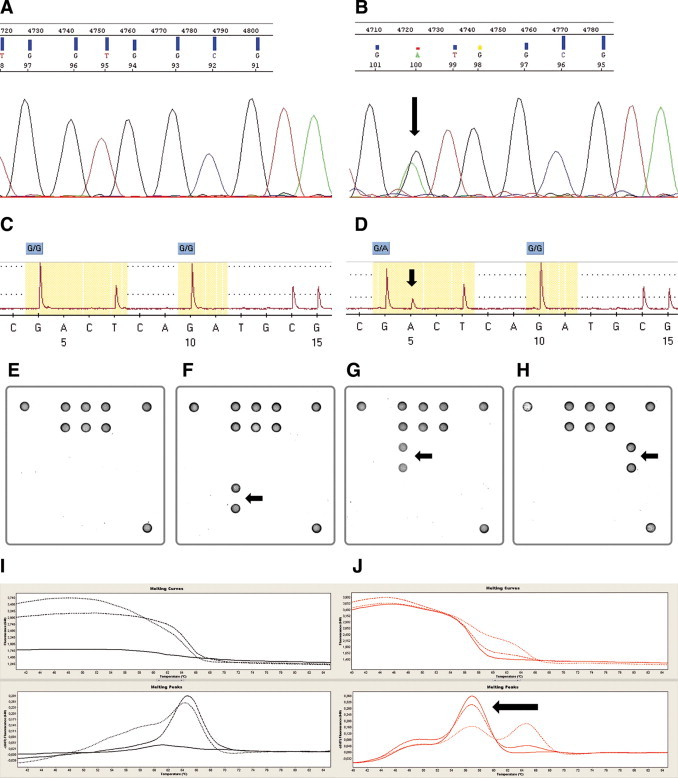
Different detection methods for KRAS mutations in codon 12/13. A and B: Sanger sequencing. Example of a wild-type (A) and a mutated (B) case (p.G12D). C and D: Pyrosequencing. Example of a wild-type (C) and a mutated (D) case (p.G12D). E–H: Array analysis. Examples of a wild-type case (E) and cases harboring a p.G13D (F), a p.G12D (G), and a p.G12C (H) mutation are presented. I and J: Melting curve analysis. Examples of a wild-type (I) and a mutated (J) case (p.G13D). Arrows indicate location of each mutation.
