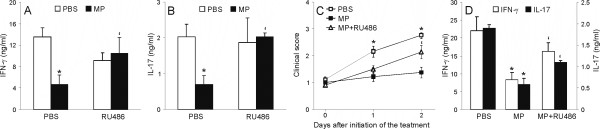
Figure 4.
RU486 prevents inhibition of IFN-γ and IL-17 by MP. (A) DA rats were immunized with SCH-CFA. Commencing on the day when first neurological signs appeared (designated as day 1) DA rats were injected daily for 3 days with methylprednisolone (MP, 50 mg/kg body weight) and/or RU486 (25 mg/kg body weight) or with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). The rats were checked daily for clinical signs of EAE. For the determination of the clinical course of EAE, 15 animals per group (out of three independent experiments) were used. (B, C) CLNC from healthy animals were stimulated with ConA (1 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of MP (10 ng/ml) and/or RU486 (5 ng/ml) for 24 hours. Cell-free supernatants of the cultures were analyzed with ELISA for IFN-γ (B) and IL-17 (C) concentrations. (D) SCC were isolated from DA rats immunized with SCH-CFA and injected with PBS, or with MP, or with MP+RU486, as described in Methods. Cell-free supernatants of cultures of SCC grown in medium for 72 hours were analyzed with ELISA for IFN-γ and IL-17 concentrations. *p < 0.05 represents a statistically significant difference between the MP and PBS treatment groups, and 'p < 0.05 represents a statistically significant difference between the MP and MP+RU486 treatment groups.