Figure 3.
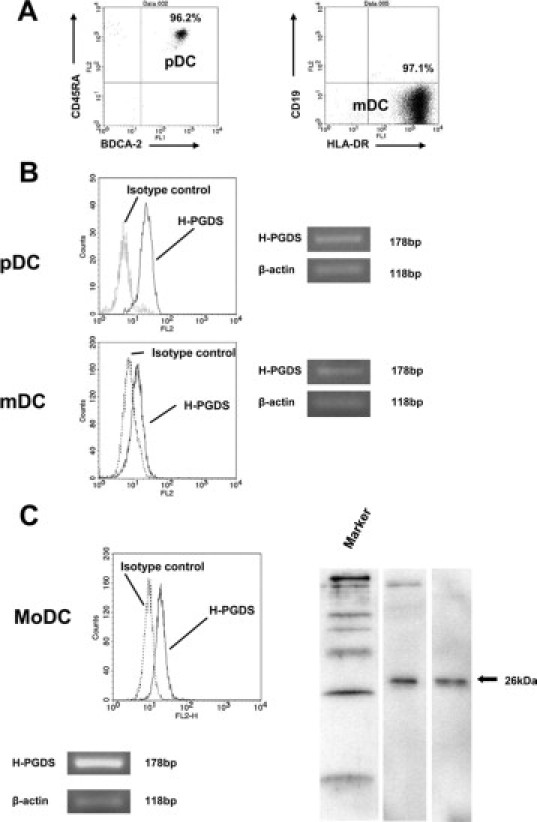
H-PGDS expression in isolated blood DCs. A: pDCs and mDCs were isolated from peripheral blood from normal donors by magnetic positive selection with CD304 (BDCA-4) for pDCs and with CD1c (BDCA-1) following the depletion of CD19+cells for mDCs. We obtained high-purity cell suspensions (>95%) as determined by the analysis of cell surface molecules, CD45RA and BDCA-2 for pDCs (left), and HLA-DR and CD19 for mDCs (right), respectively. B: Flow cytometric analysis (left) with the R-PE-conjugated mouse anti-H-PGDS mAb (EBC45) detected intracellular H-PGDS in pDCs and mDCs. RT-PCR analysis revealed the expression of H-PGDS mRNA in these cells (right). C: MoDCs generated from CD14+-blood monocytes cultured with GM-CSF/interleukin-4 expressed intracellular H-PGDS as assessed by flow cytometry with EBC45 Ab. Western blotting analysis with the monoclonal anti-human H-PGDS Ab (1E6) confirmed the presence of intracellular H-PGDS. MoDCs constitutively expressed H-PGDS mRNA. The recombinant H-PGDS prepared at the Osaka Bioscience Institute was used as a positive control protein.
