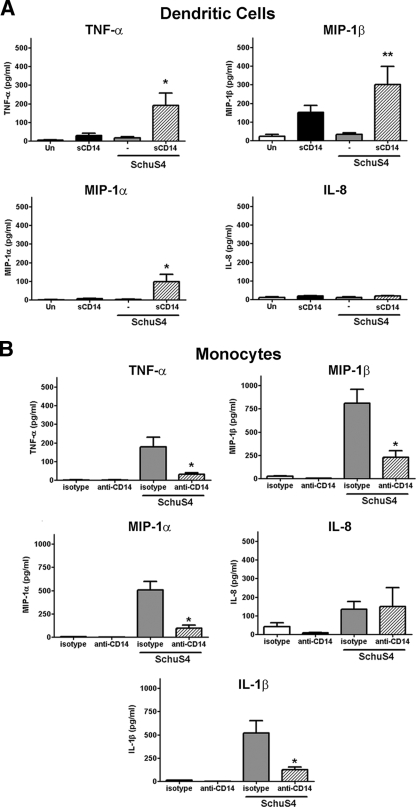
FIG. 3.
CD14 is critical for induction of cytokines during F. tularensis SchuS4 infection of human cells. Human dendritic cells (A) or primary human monocytes (B) were infected with F. tularensis SchuS4 at a MOI of 50 in the presence of sCD14 (DC), anti-CD14 (monocytes), or isotype control (monocytes). (A) sCD14 elicited secretion of significantly greater concentrations of TNF-α and MIP-1α from SchuS4-infected cells compared to the cells from all other groups (P < 0.01 [*]). sCD14 also elicited secretion of significantly more MIP-1β from SchuS4-infected cells compared to untreated, SchuS4-infected DC (Un) (P < 0.05 [**]). (B) Presence of CD14 blocking antibodies resulted in secretion of significantly less TNF-α, MIP1-α, MIP-1β, and IL-1β by SchuS4-infected monocytes compared to monocytes from other groups (P < 0.01 [*]). Data are pooled from six separate experiments, using different donors. Values are means plus SEM (error bars).