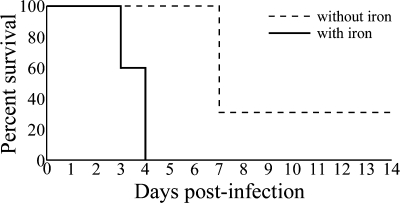
FIG. 1.
Iron supplementation to the host accelerates disease progression and produces consistent lethality following intranasal infection by KIM D27. BALB/c mice were intranasally infected with 6.8 × 106 CFU (640 LD50) KIM D27. One group received intraperitoneal injections of 50 μg inorganic iron (n = 5), and the other group (n = 6) received intraperitoneal injections of sterile water, just prior to challenge. Survival and time to death were monitored over 14 days; time to death was evaluated by the Wilcoxon rank sum test, which revealed a significant decrease in the time to death for mice treated with iron (P < 0.005).