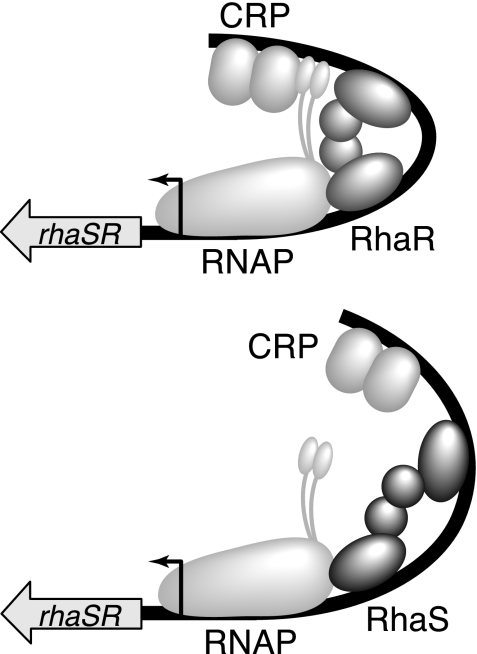
FIG. 4.
Model for RhaS negative autoregulation. Expression of the rhaSR operon in the presence of l-rhamnose. (Top) At relatively low RhaS protein concentrations, RhaR and CRP both contribute to rhaSR activation; therefore, expression is at its maximal level. CRP contacts α-CTD (shown as two small ovals connected by a flexible linker to RNAP). (Bottom) At relatively high RhaS protein concentrations, RhaS binds to the RhaR binding site, thereby replacing RhaR. RhaS contributes to rhaSR activation, but CRP does not effectively coactivate; therefore, rhaSR expression is reduced. CRP does not effectively contact α-CTD.