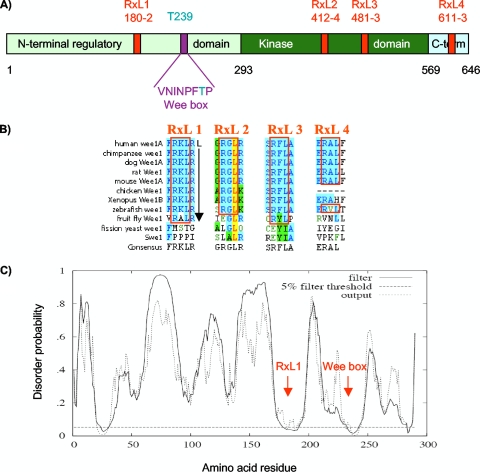
FIG. 3.
Conserved RXL sequences in Wee1. (A) Primary structure map of human somatic Wee1, with residue numbers at domain boundaries below (black): NRD (light green), kinase domain (dark green), carboxy-terminal domain (light blue), RXL sites (red, with amino acid numbers below), Wee box (single-letter amino acids), and T239 phosphorylation site (aqua). (B) RXL sequences conserved in Wee1 (blue shading). Note that RXL1 and RXL3 are conserved through the fruit fly, and RXL1 is followed by a leucine at position +5, favored in cyclin A binding sequences. The leucine in RXL2 (yellow) is predicted to be involved in packing interactions. (C) Predicted disorder plot of the Wee1 NRD from the DISOPRED server (http://bioinf.cs.ucl.uk/disopred/). The horizontal hatched line marks the 5% default false-positive rate for disordered regions, the solid filter line marks the output from DISOPRED2, and the hatched output line marks the output from a linear support vector machine classifier of lower confidence level. Positions of the RXL1 and Wee box are marked. x axis, Wee1 amino acid sequence; y axis, probability of being disordered.