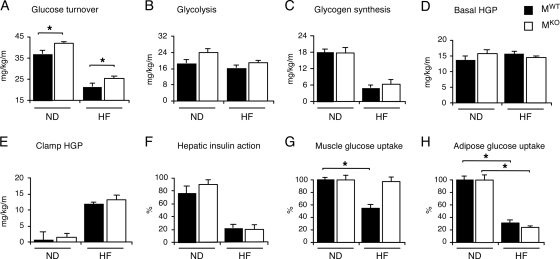
FIG. 3.
Effect of muscle-specific deficiency of JNK1 on insulin sensitivity. (A to F) Insulin sensitivity was measured using a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp with conscious chow-fed (ND) and HFD-fed (HF) MKO and MWT mice. (A) Insulin-stimulated whole-body glucose turnover. (B) Whole-body glycolysis. (C) Whole-body glycogen plus lipid synthesis. (D) Basal HGP. (E) Insulin-stimulated rate of HGP during the clamp assay. (F) Hepatic insulin action expressed as the insulin-mediated percent suppression of basal HGP. The data presented are the means ± standard errors for approximately six to nine experiments. Statistically significant differences between MKO mice and MWT mice are indicated (*, P < 0.05). (G and H) Glucose uptake in white adipose tissue (G) and gastrocnemius muscle (H) was measured in the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp study. The data are expressed as the percent suppression of glucose uptake caused by feeding of an HFD and presented as the means ± standard errors for approximately four to nine experiments. Statistically significant differences between MKO mice and MWT mice are indicated (*, P < 0.05).