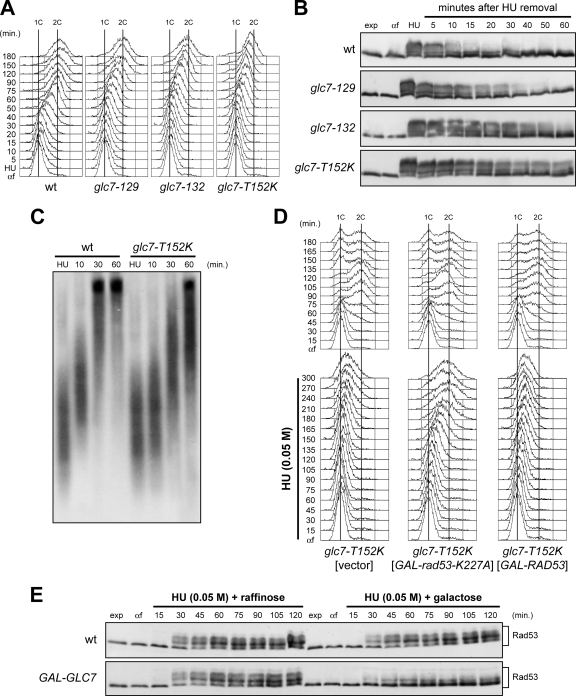
FIG. 2.
Restart of a stalled replication fork is defective in glc7 mutants, and this defect is suppressed by antagonizing Rad53 activity. (A and B) Wild-type (wt), glc7-129, glc7-132, and glc7-T152K cells were released from G1 arrest (αf) into YPD medium containing 0.2 M HU and incubated for 210 min (HU). Then, cultures were released into fresh medium, and samples were taken at the indicated times after HU removal to determine DNA content by FACS analysis (A) and to detect Rad53 by Western blot analysis with anti-Rad53 antibodies (B). (C) Immunodetection of BrdU-pulsed DNA. G1-arrested cells were released into YPgal containing 0.2 M HU plus 25 mM BrdU. After 1 h (HU), cells were chased with 2 mM thymidine into fresh medium, and DNA from samples taken at the indicated times after chase was prepared to detect BrdU-labeled DNA with anti-BrdU antibody. (D) glc7-T152K cells containing a URA3 centromeric plasmid, either empty or carrying the GAL-RAD53 or the GAL-rad53-K227A allele, were blocked in G1 with α-factor (αf) in SCraf-Ura and released into YPgal in the absence (top) or presence (bottom) of 0.05 M HU. Cell samples were collected at the indicated times after α-factor release to determine DNA content by FACS analysis. (E) Wild-type and GAL-GLC7 cells were released from G1 arrest (αf) in SCraf-Ura into YPraf or YPgal with 0.05 M HU. Cell samples were collected at the indicated times after α-factor release to detect Rad53 protein by Western blot analysis.