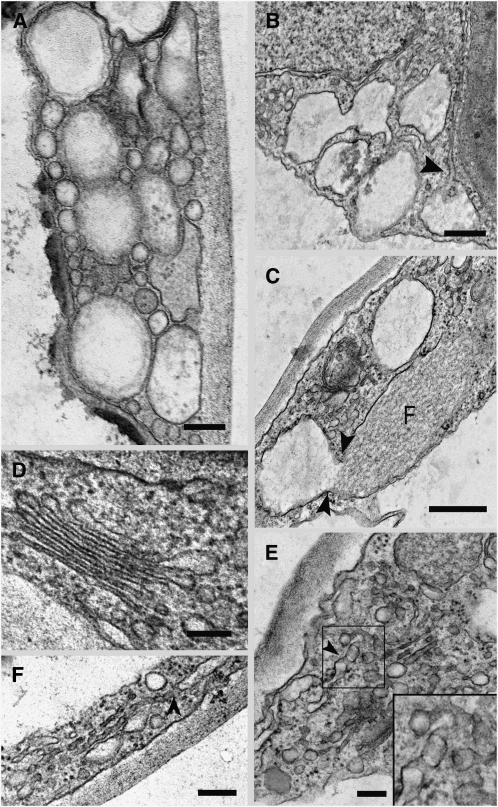
Figure 3.
Ultrastructure of the G92 Mutant.
Electron microscopy analyses of the G92 cotyledons show alteration of the ER and Golgi in the globular structures.
(A) Aggregation of different sized vesicular clusters in the cytoplasm of a G92 mutant cotyledonal leaf epidermal cell. Bar = 100 nm.
(B) Large vesicular structures in the epidermal cells are connected to the ER (arrowhead). Bar = 200 nm.
(C) Continuity between a fusiform body (F) in the lumen of the ER (Hawes et al., 2001) and a vesicular structure. Bar = 200 nm.
(D) Golgi stack in an epidermal cell of a control cotyledonal leaf from a plant stably transformed with ST-GFP. Bar = 100 nm.
(E) Disrupted Golgi stack. Golgi remnants appear to be vesicular and tubular in structure and can connect with the ER (see arrowhead). Inset shows a detail in the boxed area (magnified × 2) in the main panel. Bar = 100 nm.
(F) Disrupted Golgi stack in a G92 cotyledonal leaf epidermal cell showing apparent continuity with the ER (arrowhead). Bar = 100 nm.