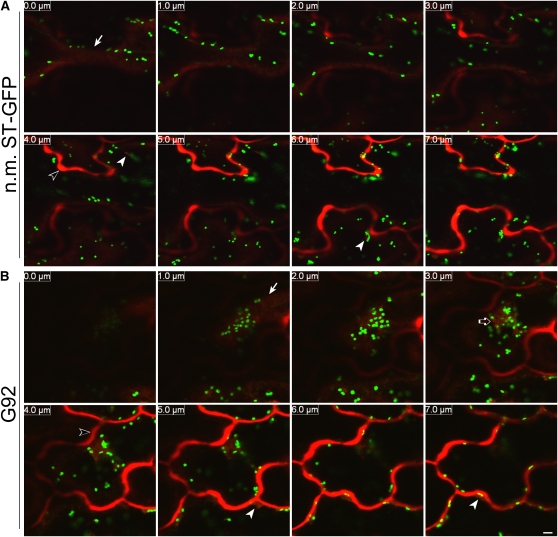
Figure 8.
The Distribution of the Soluble Marker secRFP Is Not Visibly Affected at the Level of the Bulk ER.
(A) Sequential confocal optical sections (8 × 1 μm with 0.0-μm section corresponding to the cell surface [arrow]) of the nonmutagenized T1 ST-GFP line (n.m. ST-GFP; pseudocolored green) expressing the soluble secretory marker secRFP (pseudocolored red) show that the marker reaches the apoplast (open arrowhead in the 4.0 μm panel), and it is not detectable in the cortical ER. secRFP punctae that might correspond to ER bodies are indicated by two arrowheads in the 4.0 and 6.0 μm panels. Bar = 5 μm.
(B) Images of cotyledonal epidermal cells from a G92 T1 plant transformed with secRFP, acquired using the same confocal microscope settings (confocal optical section, laser, photomultipliers, and magnification) as the control (A) show that secRFP is not retained in the cortical ER. secRFP fluorescence is clearly detectable in the apoplast (open arrowhead in the 4.0 μm panel) and at the globular structures (open arrow in the 3.0 μm panel). secRFP was also seen in some cells to accumulate in small globular structures (arrowheads in the 5.0 and 7.0 μm panels) that might either correspond to ER bodies as in the control (A) (Teh and Moore, 2007) or to the punctate structures that are sometimes visible in the ER of the G92 mutant (Figure 2B). An arrow points to the cell surface.