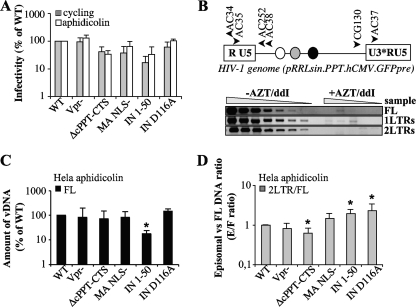
FIG. 2.
Characterization of the infectivity and nuclear import abilities of mutant viruses in HeLa cells. CA-normalized quantities of virion particles were used to infect cycling and arrested HeLa cells that had been treated with aphidicolin for 24 h prior to infection. (A) The quantity of infected GFP-positive cells was assessed at 3 days postinfection by flow cytometry (values are expressed as percentages of the WT level). For PCR, cells were lysed at 24 h postinfection, and the accumulation of reverse transcription products was analyzed by semiquantitative PCR. (B) Schematic representations of the HIV-1 genome used here and of the primers used to amplify the various viral DNA forms. For simplicity, the Rev responsive element, the cPPT-CTS, and the CMV-GFP-Wpre expression cassette are presented as white, gray, and black circles, respectively. Shown are typical results for PCRs performed with the various viral DNA forms, using threefold dilutions of cell lysates infected with WT HIV-1 in the presence or absence of RT inhibitors to ensure that quantification occurred within the linear range of the assay. Full-length (FL) products of reverse transcription (C) are expressed as percentages of the wild-type level. (D) The quantity of 2-LTR circles was normalized to the quantity of FL products for each mutant, and the 2-LTR-circle/FL-DNA ratio for the wild type was set to 1. “E/F ratio” represents the ratio of episomal to full-length products. Graphs are representative of 5 to 8 experiments. Values that are significantly different from those observed for the wild type are indicated by an asterisk (Student test; P < 0.05).