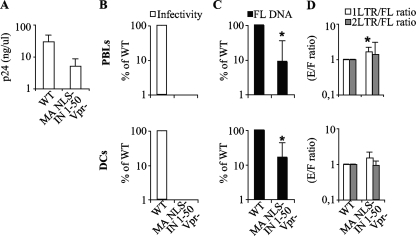
FIG. 5.
The cPPT-CTS is the major determinant of the nuclear import defect of the ΔNLS mutant. (A) The quantity of viral particles released in the supernatant following transfection of 293T cells with plasmid coding for the wild type and for a mutant virus mutated in its karyophilic elements, with the exception of the cPPT-CTS mutant (MA NLS−, IN 1-50, and Vpr), was determined by p24CA ELISA after purification. (B) Virions were used to infect PHA-IL-2-stimulated PBLs or DCs, and cells were analyzed by flow cytometry 3 to 5 days later. The graph presents data obtained with 3 to 4 independent experiments. For simplicity, data obtained with the ΔNLS mutant are omitted here and below. (C and D) PCR analysis was carried out as described in the legend to Fig. 2, and the relative quantities of FL products of reverse transcription (black bars) and the 1-LTR-circle/FL-DNA (white bars) and 2-LTR-circle/FL-DNA (gray bars) ratios were determined. Graphs present values obtained in 3 to 5 independent experiments. Values that are significantly lower than those observed for the wild type are indicated by an asterisk (Student test; P < 0.05).