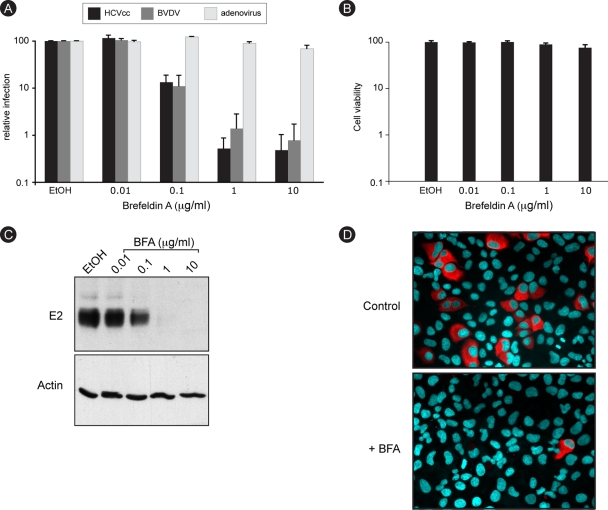
FIG. 1.
HCV infection is sensitive to BFA. (A) Huh-7 cells were infected with HCV or GFP-expressing adenovirus, and MDBK cells were infected with BVDV in the presence of 0.2% ethanol (EtOH) or increasing concentrations of BFA. BFA was present for 8 h for Huh-7 cells (HCVcc and adenovirus) or throughout the experiment for MDBK cells (BVDV). At 24 h postinfection, cells were harvested for luciferase assays (HCVcc) or fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis (BVDV and adenovirus). The luciferase activity or number of infected cells for ethanol-treated cells is expressed as 100%. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means for 4 (HCV), 6 (BVDV), or 3 (adenovirus) experiments. (B) Huh-7 cells were incubated for 8 h in the presence of 0.2% EtOH or increasing concentrations of BFA and then cultured for 18 h without drug. Viability was assessed using an MTS assay. The absorbance of the ethanol-treated sample is expressed as 100%. (C) Huh-7 cells were infected with HCVcc as for panel A. At 30 h postinfection, E2 and actin expression levels were analyzed by immunoblotting. (D) Huh-7 cells were infected for 2 h with HCVcc in the presence of 0.2% EtOH or 1 μg/ml BFA. BFA was removed at 6 h postinfection. Cells were fixed at 30 h postinfection and processed for immunofluorescence detection of E2.