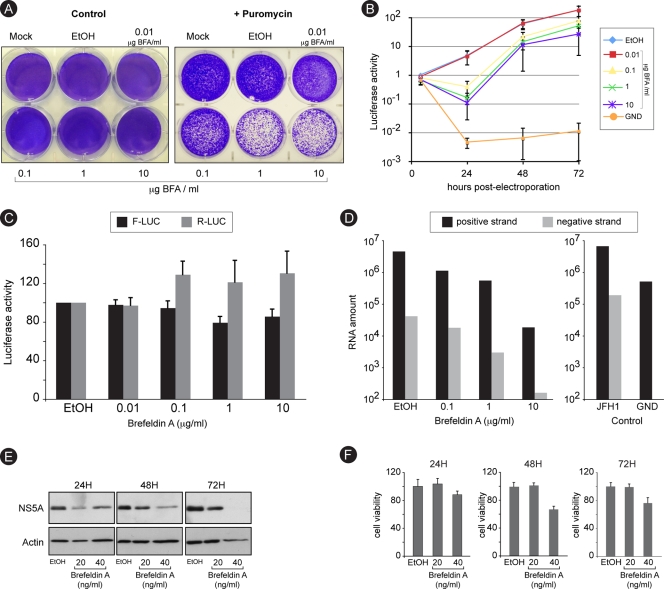
FIG. 3.
Brefeldin A inhibits RNA replication. (A) Huh-7 cells were electroporated with a recombinant HCV genome containing a deletion in E1E2 and expressing a puromycin acetyltransferase selection marker. Cells were cultured in the presence of increasing concentrations of BFA for 8 h and then in the presence or the absence of 1 μg/ml puromycin for 6 days. Cells were stained with crystal violet. (B) Huh-7 cells were electroporated with a recombinant HCV genome containing a deletion in E1E2 and expressing Renilla luciferase and were cultured in the presence of BFA for 8 h and then in the absence of the drug. For comparison, Huh-7 cells were electroporated with a nonreplicative (GND) HCV genome and cultured in the absence of BFA. Samples were harvested for luciferase assay at 4, 24, 48, and 72 h postelectroporation. The luciferase activity from ethanol-treated cells at 4 h postelectroporation is expressed as 1. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means for 3 experiments. (C) Huh-7 cells were electroporated with in vitro-transcribed and capped RNA constructs expressing firefly luciferase (F-Luc) under cap control and Renilla luciferase (R-Luc) under HCV IRES control. Cells were cultured in the presence of increasing concentrations of BFA and harvested for dual-luciferase assay at 8 h postelectroporation. (D) Huh-7 cells were infected with HCVcc, treated with increasing concentrations of BFA for 8 h, and harvested at 24 h postinfection for quantitative RT-PCR quantification of HCV plus and minus strands. To confirm the specificity of negative-strand amplification, cells electroporated with in vitro-transcribed HCV replicative (JFH1) or nonreplicative (GND) genomes were processed in parallel (control). (E and F) Huh-7 cells harboring a subgenomic replicon were cultured in the presence of the indicated concentrations of BFA. Samples were harvested after 24, 48, or 72 h of treatment for immunoblot detection of NS5A and actin (E) or for analysis of cell viability (F).