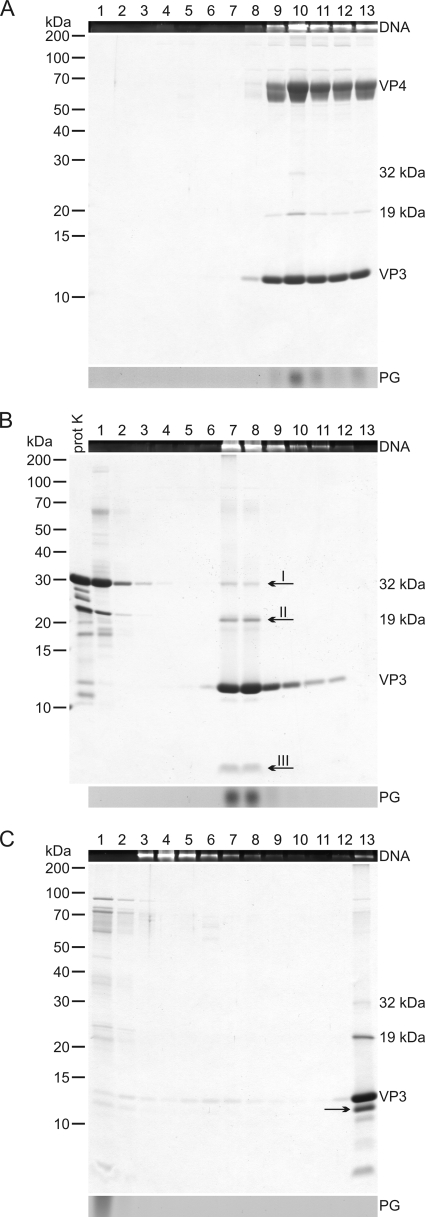
FIG. 2.
Proteinase K treatment of HRPV-1 virions and further dissociation with TX-100. (A) Untreated “2× purified” virus particles analyzed by rate zonal centrifugation in HRPV-1-buffer. (B) Particles treated with proteinase K in HRPV-1-buffer and analyzed in the same conditions as in panel A. (C) Proteinase K-treated particles further dissociated with TX-100 without a protease inhibitor and analyzed as in panel A. (A to C) After centrifugation, gradients were fractionated, and numbers at the top indicate fractions 1 to 13 from the top to the bottom (fraction 13 is the resuspended pellet). The upper panels show the presence of DNA in EtBr-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gels. The middle panels show protein compositions in Coomassie blue-stained 14% Tricine-SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Numbers on the left indicate the molecular masses (in kilodaltons) of the markers. In the lower panels lipids were analyzed by TLC, but only the PG band of the viral lipids (see Fig. 7) is indicated. In panel A, the infectivity was also determined, and the infectivity peak was in fractions 9 to 13. In panel B, a sample of proteinase K (prot K) was also included in the Tricine-SDS-PAGE, and the arrows I to III indicate the bands analyzed by N-terminal sequencing or mass spectrometry. In panel C, the PG band is distorted due to TX-100 interference, and the arrow indicates a likely digestion product of VP3.