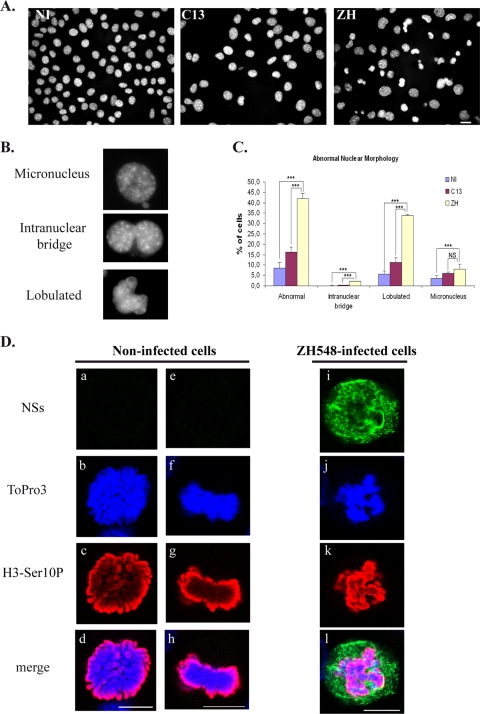
FIG. 4.
Infection with pathogenic RVFV strain ZH548 induces abnormal nuclear morphologies in murine fibroblasts. (A) Nonconfocal conventional fluorescence microscopy of L929 cells that were either not infected (NI) or infected by RVFV ZH548 strain (ZH) or by nonpathogenic clone 13 (C13) strain displaying DNA stained with Hoechst. (B) Common defects include micronuclei, intranuclear bridges, and lobulated nuclei. (C) The number of nuclei displaying abnormalities was quantified in cells that were not infected (NI) or in clone 13 (C13)- and ZH548 (ZH)-infected cells from two different experiments with n > 1,000 for each condition. The incidence of abnormal nuclei in ZH-infected was compared to uninfected cells or C13-infected cells by using the chi-square test. ***, P < 0.001; NS, not significant. (D) Single confocal sections taken through the z axis of uninfected or ZH-infected mitotic L929 cells displaying immunostaining with anti-NSs in green (a, e, and i), DNA counterstained with ToPro3 in blue (b, f, and j), immunostaining with anti-H3-Ser10P in red (c, g, and k), and the corresponding merge images (d, h, and l). Bars, 10 μm.