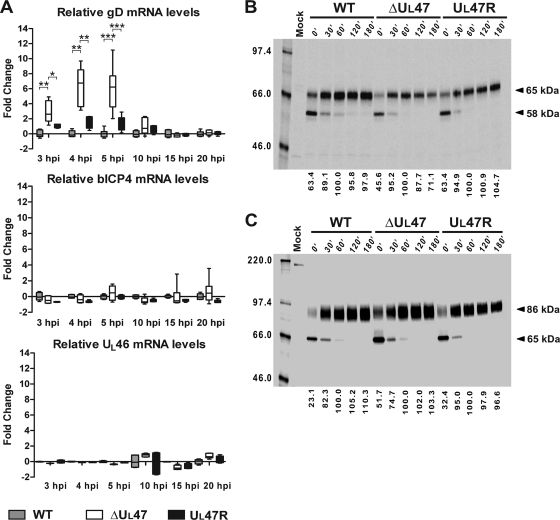
FIG. 4.
Influence of UL47 gene deletion on gD, bICP4, and UL46 mRNA levels and gD and gC protein stability. (A) Analysis of gD, bICP4, and UL46 mRNA levels during the course of infection with WT BHV-1, BHV1-ΔUL47, or BHV1-UL47R. Duplicate monolayers of MDBK cells were infected with the viruses at a MOI of 5 or mock infected, and total RNA was extracted from the cells collected at different time points after infection (from 3 h to 20 h postinfection [hpi]). After genomic DNA removal and reverse transcription, relative gD, bICP4, and UL46 mRNA levels were quantified by qPCR using 18S rRNA internal controls to normalize template input. The statistical significance of the different values is shown as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (B and C) Evaluation of gD and gC stability, respectively, in pulse-chase experiments. MDBK cells were infected for 8 h 30 min with 5 PFU/cell of WT BHV-1, BHV1-ΔUL47, or BHV1-UL47R or mock infected, pulse-labeled for 40 min with [35S]methionine/cysteine, and chased for 0, 30, 60, 120 and 180 min (180′) with medium containing nonradioactive methionine and cysteine. Each total cell lysate was divided into two equal aliquots, and paired aliquots were subjected to immunoprecipitation with either gD-specific or gC-specific MAb. The protein-antibody complexes were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The values on the right side of the panels are the molecular masses of precursor and mature forms of the proteins. The amount of mature 65-kDa gD and mature 86-kDa gC at each time point was measured by densitometry. Since precursor polypeptides were completely processed into mature forms after 60 min of chase, the obtained values were compared to the corresponding values for 60 min of chase that were set at 100% (bottom of the panels). The values on the left side of the panels are molecular masses in kilodaltons.