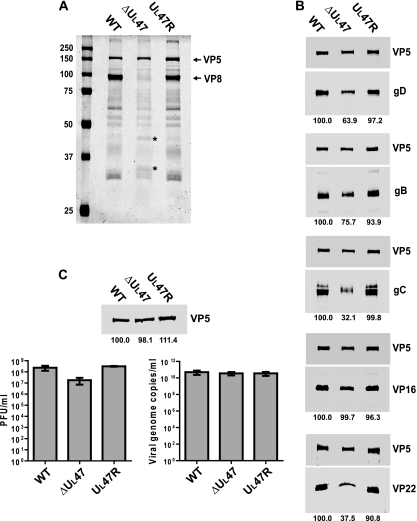
FIG. 5.
Analysis of the influence of the UL47 gene deletion on virion composition and infectivity. (A) Solubilized proteins of purified extracellular virions of WT BHV-1, BHV1-ΔUL47, or BHV1-UL47R were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. The positions of VP5 and VP8 proteins are indicated to the right of the gel. The bands that are present at larger amounts in the BHV1-ΔUL47 protein profile are indicated by asterisks. The values on the left side of the panel are molecular masses in kilodaltons. (B) The same samples shown in panel A were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against gD, gB, gC, VP16, and VP22. The major nucleocapsid protein, VP5, was simultaneously detected on each membrane to normalize the protein input. Blots were analyzed by densitometry, and average normalized values of two independent experiments are shown as percentages of the corresponding values for the WT virus (below the blots). (C) Relative particle-to-PFU ratios. The volumes of the purified virion preparations were adjusted to normalize the VP5 protein content according to the densitometry results (top panel). The densitometry values expressed as a percentage of WT virus are averages from samples run in duplicate, whereas only one set of bands is shown. The concentration of infectious virus in the obtained preparations was determined by plaque assay (bottom left panel) and compared to the relative number of viral genome copies measured by qPCR (bottom right panel).