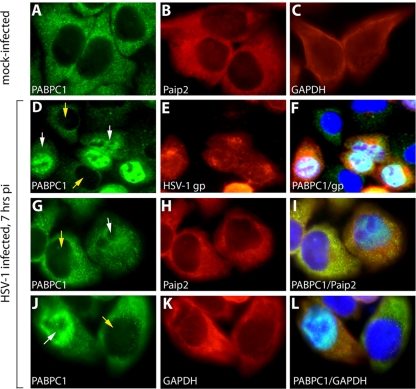
FIG. 2.
HSV-1 infection results in PABPC1 redistribution to the nucleus. HeLa cells were mock infected (A to C) or infected at an MOI of 10 with HSV-1 for 7 h (D to L). PABPC1 (A), Paip2 (B) and GAPDH control (C) are shown in mock-infected HeLa cells. HSV-1 infection results in PABPC1 relocalization to the nucleus in infected (D; white arrow) but not uninfected (D; yellow arrows) cells in the same culture. (E) Infection was confirmed by staining with anti-HSV-1 glycoprotein antibody (gp). (F) Overlapping nuclear PABPC1/HSV-1 glycoprotein is visible in the merged image. PABPC1 (G and J), Paip2 (H), and GAPDH (K) are shown in presumably uninfected cells (yellow arrow) and infected cells (white arrow). Merged images show overlapping nuclear PABPC1/DAPI signal and markedly reduced cytoplasmic PABPC1 signal only in infected cells (I and L). pi, postinfection.