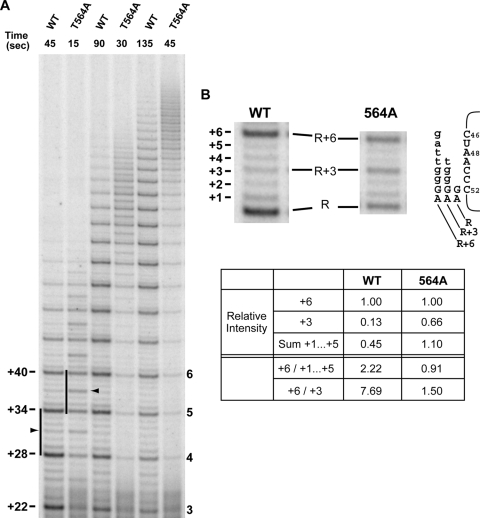
FIG. 6.
Competitive primer challenge assay with wild-type and T564A mutant hTERT. (A) Primer extension reactions were carried out under competitor challenge conditions. Following 5-min binding of radiolabeled substrate primer, extension reactions were initiated and chased with excess cold competitor primer. Postchase aliquots were taken at the time points (in seconds) indicated and analyzed via PAGE. The black arrowheads indicate product accumulation prior to copying template residue A48. Regions of active polymerization (12) for wild-type hTERT (containing the 5th full repeat) and 564A hTERT (containing the 6th full repeat) are indicated by the black bars. The numbers to the left of the gel (+22, +28, etc.) indicate positions of products corresponding to the end of each round of template copying (expressed as number of nucleotides added to the primer), with the number of full repeats shown to the right of the gel. (B) Enlarged view of the active polymerization regions marked in panel A. Schematic diagram indicates alignments of repeat + 3 (R + 3) and R + 6 major synthesis products with the template RNA. Nucleotides added during each round of primer elongation are shown in lowercase type. hTR nucleotide positions are indicated next to the template sequence. Relative band intensities of the +3 (R + 3), +6 (R + 6), and sum of +1 to +5 products in the repeats shown were quantified via phosphorimaging.