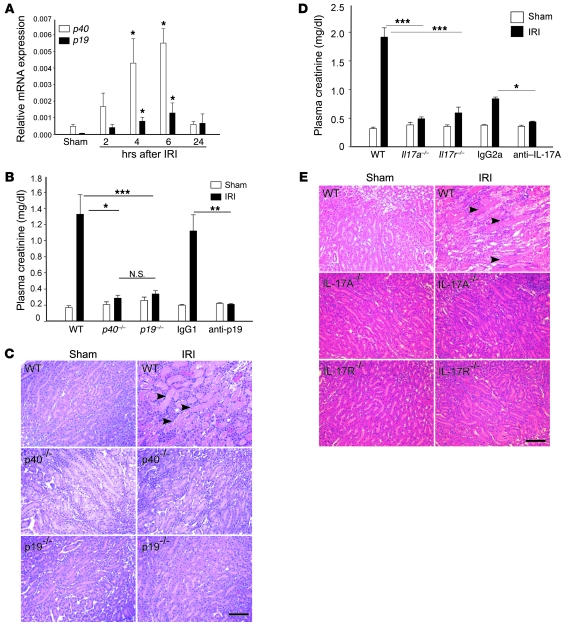
Figure 1. The IL-23/IL-17 pathway contributes to kidney IRI.
(A) mRNA levels of p40 and p19 were measured by real-time PCR in kidneys after 28 minutes of ischemia and exposure to different times of reperfusion. Values are expressed as relative gene expression (compared with GAPDH) in sham-operated samples and IRI samples following different times of reperfusion. n = 3–5. *P < 0.05 compared with sham. (B) Plasma creatinine was measured as an indication of kidney function in mice exposed to sham operation or IRI (ischemia followed by 24 hours of reperfusion). IgG1, WT mice that received 100 μg IgG1 isotype control 18 hours prior to kidney IRI; anti-p19, WT mice that received anti-p19 mAb treatment 18 hours prior to kidney IRI. n = 4–18; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (C) Representative morphology (by H&E staining) of kidney outer medulla from WT, p40–/–, and p19–/– sham and IRI mice. (D) Plasma creatinine in WT, Il17r–/–, and Il17a–/–, IgG2a, and anti–IL-17A sham and IRI mice after 24 hours of reperfusion. n = 4–9; *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001. (E) H&E staining of kidney outer medulla from WT, Il17r–/–, and Il17a–/– sham and IRI mice after 24 hours of reperfusion. In C and E, arrowheads indicate necrotic tubules. Scale bars: 100 μm. Values are mean ± SEM.