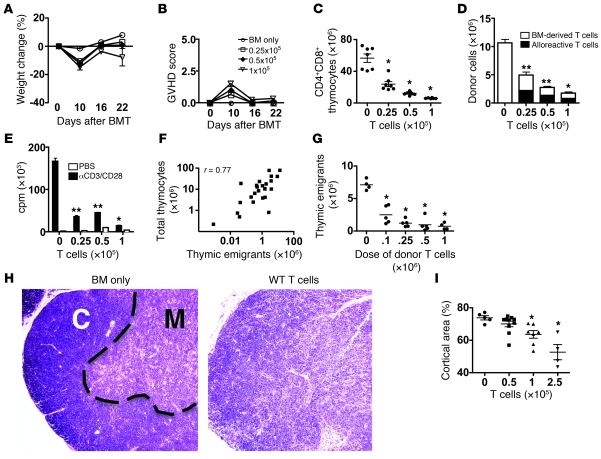
Figure 1. Clinical GVHD correlates with tGVHD and thymic function of B6 → BALB/c (8.5 Gy) mice.
(A) Weight loss and (B) GVHD score. n = 6–7/group. (C) Donor BM-derived CD4+CD8+ thymocyte numbers on day 22. Dots represent groups of animals. *P < 0.05 versus TCD-BM control. n = 6–7/group. (D) Total donor splenic T cells on day 22. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001 versus control; P values are shown for donor BM-derived T cells. n = 6–7/group. (E) Proliferation of splenic T cells after stimulation with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 on day 22. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001 versus control. TCD-BM only and 0.25 × 105 T cells, n = 12; 0.5 × 105 T cells, n = 6; 1 × 105 T cells, n = 3. (F) Linear regression of log-transformed thymic cellularity versus log-transformed splenic RTE numbers. Squares represent individual animals combined (n = 24) across all groups. One of two identical experiments is shown. r, regression coefficient. (G) RTEs versus the dose of donor T cells on day 42 after transplant. Dots represent individual animals. n = 4–5/group. *P < 0.05 versus recipients of TCD-BM only. (H) Histopathology (H&E) of paraffin-fixed thymus sections on day 28 (no GVHD, BM only; GVHD, BM plus 0.25 × 106 WT T cells). The dotted line indicates the corticomedullary junction. C, cortex; M, medulla. Original magnification, ×50. n = 5/group. Representative sections are shown. (I) Quantification of cortical area (% of total area) on day 28. Average of 3 sections of each organ (50 μm apart). Symbols represent individual animals. n = 4–7/group. *P = 0.01 versus recipients of TCD-BM only. All horizontal bars indicate the mean. All values are mean ± SEM.